Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A conducting sphere of radius 10 cm has an unknown charge. If the electric field 20 cm from the centre of the sphere is 1.5 × 103 N/C and points radially inward, what is the net charge on the sphere?
Solution
Electric field intensity (E) at a distance (d) from the centre of a sphere containing net charge q is given by the relation,
`"E" = 1/(4piε_0r^2)`
Where,
q = Net charge = 1.5 × 103 N/C
d = Distance from the centre = 20 cm = 0.2 m
ε0 = Permittivity of free space
And, `1/(4piε_0)` = 9 × 109 N m2 C−2
∴ `"q" = "E"(4piε_0)"d"^2`
= `(1.5xx10^3xx(0.2)^2)/(9xx10^9)`
= 6.67 × 10-9 C
Charge is negative, or anti-static, because the electric field is inward-pointing.
q = - 6.67 nC.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A point charge q is placed in a cavity in a metal block. If a charge Q is brought outside the metal, will the charge q feel an electric fore?
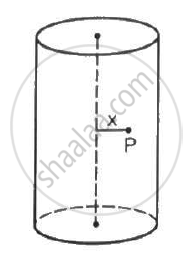
A long cylindrical volume contains a uniformly distributed charge of density ρ. Find the electric field at a point P inside the cylindrical volume at a distance x from its axis (see the figure).
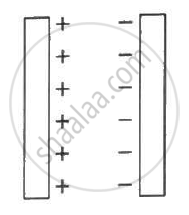
Two large conducting plates are placed parallel to each other and they carry equal and opposite charges with surface density σ as shown in the figure. Find the electric field (a) at the left of the plates (b) in between the plates and (c) at the right of the plates.
A positively charged glass rod is brought close to a metallic rod isolated from ground. The charge on the side of the metallic rod away from the glass rod will be ______.
Choose the correct option.
A charge of + 7 μC is placed at the centre of two concentric spheres with radius 2.0 cm and 4.0 cm respectively. The ratio of the flux through them will be
When 1019 electrons are removed from a neutral metal plate through some process, the electric charge on it is ______
Ionization of a neutral atom is the ______.
Assertion: The positive charge particle is placed in front of a spherical uncharged conductor. The number of lines of forces terminating on the sphere will be more than those emerging from it.
Reason: The surface charge density at a point on the sphere nearest to the point charge will be negative and maximum in magnitude compared to other points on the sphere.
A solid sphere of radius R1 and volume charge density `rho = rho_0/"r"` is enclosed by a hollow sphere of radius R2 with negative surface charge density σ, such that the total charge in the system is zero. `rho_0` is a positive constant and r is the distance from the center of the sphere. The ratio R2/R1 is ______.
Two charges q1 and q2 are placed in vacuum at a distance d and the force acting between them is F. If a medium of dielectric constant 4 is introduced around them, the force now will be ______.
Which of the following graphs shows the variation of electric field E due to a hollow spherical conductor of radius R as a function of distance from the centre of the sphere?
Two identical conducting spheres A and B, carry equal charge. They are separated by a distance much larger than their diameter, and the force between them is F. A third identical conducting sphere, C, is uncharged. Sphere C is first touched to A, then to B, and then removed. As a result, the force between A and B would be equal to ______.
A particle of mass m and charge q is placed at rest in a uniform electric field E and then released. The kinetic energy gained by the particle after moving a distance of y will be ______.
The electrostatic potential inside a charged spherical ball is given by `Phi = ar^2 + b`, where r is the distance from the centre a, and b are constants. Then the charge density inside the ball is ______.
Two particles A and B having the same mass have charges +q and +4q, respectively. When they are allowed to fall from rest through the same electric potential difference the ratio of their speeds vA to vB will become ______.
The potential at a point x (measured in µm) due to some charges situated on the X-axis is given by v(x) = `20/((x^2 - 4)` V. The electric field E at x = 4 µm is given by ______.
