Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A constant force of 2⋅5 N accelerates a stationary particle of mass 15 g through a displacement of 2⋅5 m. Find the work done and the average power delivered.
Solution
Given:
\[ = 2 . 5 \times 2 . 5 = 6 . 25 J\]
Acceleration of the particle is,
\[a = \frac{F}{m} = \frac{2 . 5}{0 . 015}\]
\[ = \frac{500}{3} \text{ m/ s} ^2\]
Applying the work-energy principle for finding the final velocity of the particle,
\[\frac{1}{2}m v^2 - 0 = 6 . 25\]
\[ \Rightarrow \nu = \sqrt{\frac{6 . 25 \times 2}{0 . 15}} = 28 . 86 \text{ m/s }\]
So, time taken by the particle to cover 2.5 m distance,
\[t = \frac{\nu - u}{\alpha} = \frac{\left( 28 . 86 \right) \times 3}{500}\]
\[ \therefore \text{ Average power } = \frac{W}{t}\]
\[ = \frac{6 . 25 \times 500}{\left( 28 . 86 \right) \times 3} = 36 . 1 W\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
List all the forces acting on the block B in figure.
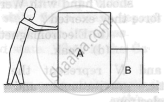
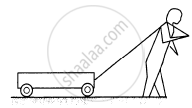
Figure shows a boy pulling a wagon on a road. List as many forces as you can which are relevant with this figure. Find the pairs of forces connected by Newton's third law of motion.
Let E, G and N represent the magnitudes of electromagnetic gravitational and nuclear forces between two electrons at a given separation. Then
If all matters were made of electrically neutral particles such as neutrons,
(a) there would be no force of friction
(b) there would be no tension in the string
(c) it would not be possible to sit on a chair
(d) the earth could not move around the sun.
At what distance should two charges, each equal to 1 C, be placed so that the force between them equals your weight ?
A body builder exerts a force of 150 N against a bullworker and compresses it by 20 cm. Calculate the spring constant of the spring in the bullworker.
Two charged particles placed at a separation of 20 cm exert 20 N of Coulomb force on each other. What will be the force of the separation is increased to 25 cm?
A small block of mass m is kept on a rough inclined surface of inclination θ fixed in an elevator. the elevator goes up with a uniform velocity v and the block does not slide on the wedge. The work done by the force of friction on the block in time t will be
A block of mass m slides down a smooth vertical circular track. During the motion, the block is in
A particle moves from a point \[\overrightarrow{r}_1 = \left( 2 m \right) \overrightarrow{ i } + \left( 3 m \right) \overrightarrow{ j } \] to another point
\[\overrightarrow{r}_2 = \left( 3 m \right) \overrightarrow{ i } + \left( 2 m \right) \overrightarrow{ j } \] acts on it. Find the work done by the force on the particle during the displacement.
A force \[F = \alpha + bx\] acts on a particle in the x-direction, where a and b are constants. Find the work done by this force during a displacement from x = 0 to x = d.
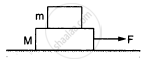
A block of mass m is kept over another block of mass M and the system rests on a horizontal surface (In the following figure). A constant horizontal force F acting on the lower block produces an acceleration \[\frac{F}{2 \left( m + M \right)}\] in the system, and the two blocks always move together. (a) Find the coefficient of kinetic friction between the bigger block and the horizontal surface. (b) Find the frictional force acting on the smaller block. (c) Find the work done by the force of friction on the smaller block by the bigger block during a displacement d of the system.
A block of weight 100 N is slowly moved up a smooth incline of inclination 37° by a person. Calculate the work done by the person in moving the block through a distance of 2 m, if the driving force is (a) parallel to the incline and (b) in the horizontal direction.
A uniform chain of mass m and length l overhangs a table with its two third part on the table. Find the work to be done by a person to put the hanging part back on the table.
A block of mass 1 kg is placed at point A of a rough track shown in figure following. If slightly pushed towards right, it stops at point B of the track. Calculate the work done by the frictional force on the block during its transit from A to B.

A block of mass m is taken from A to B slowly under the action of a constant force R Work done by this force is ______.

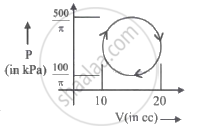
Work done by gas in cyclic process is ______ J.
A cylinder of area 300 cm2 and length 10 cm made of material of specific gravity 0.8 is floated in water with its axis vertical. It is then pushed downward, so as to be just immersed. The work done by the agent who pushes the cylinder into the water is ______ J.
