Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A free neutron beta-decays to a proton with a half-life of 14 minutes. (a) What is the decay constant? (b) Find the energy liberated in the process.
(Use Mass of proton mp = 1.007276 u, Mass of `""_1^1"H"` atom = 1.007825 u, Mass of neutron mn = 1.008665 u, Mass of electron = 0.0005486 u ≈ 511 keV/c2,1 u = 931 MeV/c2.)
Solution
Given:
Half-life period of free neutron beta-decays to a proton, `T_"1/2"` = 14 minutes
Half-life period , `T_"1/2" = 0.6931/lambda`
Here, `lambda` = Decay constant
`therefore lambda = 0.693/(14 xx 60)`
= `8.25 xx 10^-4 "S"^-1`
If mp is the mass of proton, let mn and me be the mass of neutron and mass of electron, respectively.
`therefore "Energy liberated" , E = [m_n - (m_p + m_e)] c^2`
= `[1.008665 "u" - (1.007276 + 0.0005486) "u"]c^2`
= `0.0008404 xx 931 "MeV"`
= `782 "keV"`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
For the `beta^+` (positron) emission from a nucleus, there is another competing process known as electron capture (electron from an inner orbit, say, the K−shell, is captured by the nucleus and a neutrino is emitted).
\[\ce{e+ + ^A_Z X -> ^A_{Z - 1}Y + \text{v}}\]
Show that if `beta^+` emission is energetically allowed, electron capture is necessarily allowed but not vice−versa.
Consider the D−T reaction (deuterium−tritium fusion)
\[\ce{^2_1H + ^3_1H -> ^4_2He + n}\]
Calculate the energy released in MeV in this reaction from the data:
`"m"(""_1^2"H")`= 2.014102 u
`"m"(""_1^3"H")`= 3.016049 u
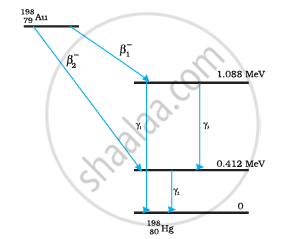
Obtain the maximum kinetic energy of β-particles, and the radiation frequencies of γdecays in the decay scheme shown in Fig. 13.6. You are given that
m (198Au) = 197.968233 u
m (198Hg) =197.966760 u
Write the basic nuclear process underlying β+ and β– decays.
Write the β-decay of tritium in symbolic form.
Write the basic nuclear process of neutron undergoing β-decay.
Why is the detection of neutrinos found very difficult?
What is the difference between cathode rays and beta rays? When the two are travelling in space, can you make out which is the cathode ray and which is the beta ray?
During a negative beta decay,
Ten grams of 57Co kept in an open container beta-decays with a half-life of 270 days. The weight of the material inside the container after 540 days will be very nearly
Consider a sample of a pure beta-active material.
Complete the following decay schemes.
(a) `"" _88^226Ra → alpha+`
(b) `""_8^19O → _9^19F+`
(c) `""_13^25Al → ""_12^25Mg+`
A free neutron decays into ______.
