Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A population of 200 fruit flies is in Hardy Weinberg equilibrium. The frequency of the allele (a) 0.4. Calculate the following:
The number of homozygous recessive fruit flies.
Solution
In Hardy Weinberg, p2 + 2pq + q2 = 1, where 'p2' is the frequency of the homozygous dominant genotype (AA), '2pq' is the frequency of the heterozygous genotype (Aa), and 'q2' is the frequency of the homozygous recessive genotype (aa).
Given:
q = 0.4
We know p + q = 1
p = 1 − q
p = 1 − 0.4
p = 0.6
number of homozygous recessive fruit flies is
As, q2(aa) = (0.4)2
= 0.16
= 0.16 × 200
= 32
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
What does the following equation represent? Explain.
p2 + 2pq + q2 = 1
Hardy Weinberg's principle explains ______
The factor that leads to the Founder effect in a population is ______
For the MN-blood group system, the frequencies of M and N alleles are 0.7 and 0.3, respectively. The expected frequency of MN-blood group bearing organisms is likely to be ______.
Which type of selection explains industrial melanism observed in moth, Biston bitularia ______.
Name the law that states that the sum of allelic frequencies in a population remains constant. What are the five factors that influence these values?
The graphs below show three types of natural selection. The shaded areas marked with arrows show the individuals in the population who are not selected. The dotted vertical lines show the statistical means.
 |
 |
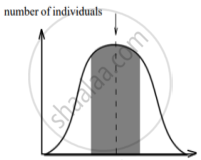 |
| character Graph A |
character Graph B |
character Graph C |
- What names are given to the types of selection shown in graphs A, B and C?
- After the selection has operated for several generations in the above populations indicated as, Graph A, B and C, graphically illustrate the probable results.
A population of 200 fruit flies is in Hardy Weinberg equilibrium. The frequency of the allele (a) 0.4. Calculate the following:
Frequency of the allele (A).
A population of 200 fruit flies is in Hardy Weinberg equilibrium. The frequency of the allele (a) 0.4. Calculate the following:
The number of homozygous dominant fruit flies.
A population of 200 fruit flies is in Hardy Weinberg equilibrium. The frequency of the allele (a) 0.4. Calculate the following:
The number of carrier fruit flies.
