Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A rod of magnetic material of cross-section 0.25 cm2 is placed in a magnetizing field of intensity 4000 A/m-1. The magnetic flux passing through the rod is 25 × 10-6 Wb. Find out
(a) relative permeability
(b) magnetic susceptibility and
(c) magnetisation of the rod.
Solution
Given: A = 0.25 cm2 = 25 × 10-6 m2
H = 4000 A m-1, Φ = 25 × 10-6 Wb
Magnetic induction is
B =
= 1 Wb/m2
(a) B = μ0μrH
∴ The relative permeability of the material,
= 198.91 = 199
(b)
∴ The magnetic susceptibility of the material,
= 199 - 1
= 198
(c)
The magnetization of the rod,
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
An iron rod of the area of cross-section 0.1m2 is subjected to a magnetizing field of 1000 A/m. Calculate the magnetic permeability of the iron rod. [Magnetic susceptibility of iron = 59.9, magnetic permeability of vacuum = 4π x 10-7 S. I. unit]
Distinguish between diamagnetic and paramagnetic substances
A meter gauge train is heading north with speed 54 km/hr in earth's magnetic field 3 x 10-4T. The e.m.f. induced across the axle joining the wheels is ..........
(a) 0.45 mV
(b) 4.5 mV
(c) 45 mV
(d) 450 m V
Explain Curie’s law for a paramagnetic substance.
Which of the following substances are para-magnetic?
Bi, Al, Cu, Ca, Pb, Ni
The susceptibility of a magnetic material is − 2.6 × 10−5. Identify the type of magnetic material and state its two properties.
A tangent galvanometer shows a deflection of 45° when 10 mA of current is passed through it. If the horizontal component of the earth's magnetic field is
The magnetic susceptibility of platinum is 0.0001. It's relative permeability is:
Two substances A and B have their relative permeability slightly greater and slightly less than 1 respectively. What do you conclude about A and B as far as their magnetic materials are concerned?
Answer the following question.
Write three points of differences between para-, dia- and ferromagnetic materials, giving one example for each.
Identify the following magnetic materials :
Which of the following statements is correct for diamagnetic materials?
Choose the correct option:
A rectangular magnet suspended freely has a period of oscillation equal to T. Now it is broken into two equal halves (each having half of the original length) and one piece is made to oscillate freely. Its period of oscillation is T′, the ratio of T′/T is ______.
The magnetic susceptibility of a paramagnetic material at - 73 °C is 0.0075. Its value at -173 °C will be ______.
Magnetic material can be easily magnetized if magnetic susceptibility is ______.
If a magnetic field is applied to a liquid in one arm of a narrow U-tube, the liquid level in that arm is lowered. The liquid in U-tube arm is ______.
The magnetic property of magnetic substance is associated with ____________.
Above the curie temperature the susceptibility of ferromagnetic substance varies ____________.
A short bar magnet has a magnetic moment of 0.48 J T−1. Give the direction and magnitude of the magnetic field produced by the magnet at a distance of 10 cm from the centre of the magnet on
- the axis,
- the equatorial lines (normal bisector) of the magnet.
Which graph shows the variation of magnetic susceptibility (
Why is diamagnetism, in contrast, almost independent of temperature?
Would the maximum possible magnetisation of a paramagnetic sample be of the same order of magnitude as the magnetisation of a ferromagnet?
A certain region of space is to be shielded from magnetic fields. Suggest a method.
The coercivity of a small magnet where the ferromagnet gets demagnetized is 3 × 103 Am–1. The current required to be passed in a solenoid of length 10 cm and number of turns 100, so that the magnet gets demagnetized when inside the solenoid, is ______.
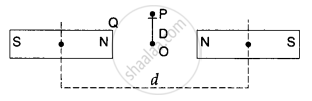
Two identical bar magnets are fixed with their centres at a distance d apart. A stationary charge Q is placed at P in between the gap of the two magnets at a distance D from the centre O as shown in the figure. The force on the charge Q is ______.
When a ferromagnetic material is created above its curie temperature
A hydrogen atom is paramagnetic. A hydrogen molecule is
Most of the substance show which of the magnetic property:-
If a charged particle at rest experience no electromagnetic force
The universal property of all substances is ______.
According to the Atomic theory, on heating a magnet, the thermal energy of the elementary magnet ______
A long solenoid has 1000 turns per metre and carries a current of 1 A. It has a soft iron core of µr = 1000. The core is heated beyond the Curie temperature, Tc.
- The H field in the solenoid is (nearly) unchanged but the B field decreases drastically.
- The H and B fields in the solenoid are nearly unchanged.
- The magnetisation in the core reverses direction.
- The magnetisation in the core diminishes by a factor of about 108.
Essential difference between electrostatic shielding by a conducting shell and magnetostatic shielding is due to ______.
- electrostatic field lines can end on charges and conductors have free charges.
- lines of B can also end but conductors cannot end them.
- lines of B cannot end on any material and perfect shielding is not possible.
- shells of high permeability materials can be used to divert lines of B from the interior region.
Magnetic susceptibility for a paramagnetic and diamagnetic materials is respectively ______.
An ammeter of resistance R gives a full-scale deflection when a current of 2 A passes through it. If it is measured with a maximum current of 10 A, the required shunt is ______.
- Assertion (A): Diamagnetic substances exhibit magnetism.
- Reason (R): Diamagnetic materials do not have a permanent magnetic dipole moment.
Which of the following has a permeability less than that of free space?
The relative magnetic permeability of a substance X is slightly less than unity and that of substance Y is slightly more than unity, then ______.
Explain the Domain theory in brief.
Explain the meaning of the following statement:
Curie temperature for soft iron is 770°C.
