Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The frequency and intensity of a light source are doubled. Consider the following statements.
(A) The saturation photocurrent remains almost the same.
(B) The maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons is doubled.
Options
A and B are true.
A is true but B is false.
A is false but B is true.
A and B are false.
Solution
A is true but B is false.
Saturated current varies directly with the intensity of light. As the intensity of light is increased, a large number of photons fall on the metal surface. As a result, a large number of electrons interact with the photons. As a result, the number of emitted electrons increases and, hence, the current also increases.
At the same time, the frequency of the light source also increases.Also, with the increase in frequency of light, the stopping potential increases as well. This will reduce the current. The combined effect of these two is that the current will remain the same
Hence, A is true.
From the Einstein's photoelectric equation.
`K_max = hv - varphi`
Where `K_max` = kinetic energy of electron
v = frequency of light
`varphi` = work function of metal
It is clear from the above equation. As the frequency of light source is doubled, kinetic energy of electron increases. But, it becomes more than the double.
Hence, B is false.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
In an experiment on the photoelectric effect, the slope of the cut-off voltage versus the frequency of incident light is found to be 4.12 × 10−15 Vs. Calculate the value of Planck’s constant.
The work function for a certain metal is 4.2 eV. Will this metal give photoelectric emission for incident radiation of wavelength 330 nm?
Light of wavelength 488 nm is produced by an argon laser which is used in the photoelectric effect. When light from this spectral line is incident on the emitter, the stopping (cut-off) potential of photoelectrons is 0.38 V. Find the work function of the material from which the emitter is made.
point out any two characteristic properties of photons on which Einstein’s photoelectric equation is based ?
Define the terms (i) ‘cut-off voltage’ and (ii) ‘threshold frequency’ in relation to the phenomenon of photoelectric effect.
Using Einstein’s photoelectric equation shows how the cut-off voltage and threshold frequency for a given photosensitive material can be determined with the help of a suitable plot/graph.
A non-monochromatic light is used in an experiment on photoelectric effect. The stopping potential
The electric field at a point associated with a light wave is `E = (100 "Vm"^-1) sin [(3.0 xx 10^15 "s"^-1)t] sin [(6.0 xx 10^15 "s"^-1)t]`.If this light falls on a metal surface with a work function of 2.0 eV, what will be the maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons?
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
A monochromatic light source of intensity 5 mW emits 8 × 1015 photons per second. This light ejects photoelectrons from a metal surface. The stopping potential for this setup is 2.0 V. Calculate the work function of the metal.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
Consider the situation of the previous problem. Consider the faster electron emitted parallel to the large metal plate. Find the displacement of this electron parallel to its initial velocity before it strikes the large metal plate.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
How does one explain the emission of electrons from a photosensitive surface with the help of Einstein’s photoelectric equation?
Choose the correct answer from given options
Photons of frequency v are incident on the surface of two metals A and B of threshold frequency 3/4 v and 2/3 v, respectively. The ratio of maximum kinetic energy of electrons emitted from A to that from B is
According to Einstein's photoelectric equation, the plot of the kinetic energy of the emitted photoelectrons from a metal versus the frequency of the incident radiation gives a straight line, whose slope ______.
Each photon has the same speed but different ______.
The minimum energy required to remove an electron is called ______.
A student performs an experiment on photoelectric effect, using two materials A and B. A plot of Vstop vs ν is given in Figure.
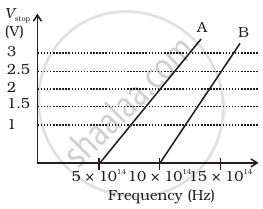
- Which material A or B has a higher work function?
- Given the electric charge of an electron = 1.6 × 10–19 C, find the value of h obtained from the experiment for both A and B.
Comment on whether it is consistent with Einstein’s theory:
The photon emitted during the de-excitation from the first excited level to the ground state of a hydrogen atom is used to irradiate a photocathode in which the stopping potential is 5 V. Calculate the work function of the cathode used.
