Advertisements
Advertisements
Questions
An object is placed at a distance of 10 cm from a convex mirror of focal length 15 cm. Find the position and nature of the image.
An object is placed at a distance of 10 cm from a convex mirror of focal length 15 cm. Find the position of the image formed by the mirror.
Solution
According to the mirror formula,
`1/"f" = 1/"v" + 1/"u"`
Where,
f is the focal length of the mirror,
u is the object distance (distance of the object from the mirror) and
v is the image distance (distance of the image from the mirror).
The focal length of a convex mirror, f = 15 cm
Object distance, u = -10 cm
image distance (v) =?
`1/"v" = 1/"f" - 1/"u"`
`1/"v" = 1/15 - 1/(-10)`
`1/"v" = -1/15 + 1/10`
`1/"v" = (2 + 3)/30`
`1/"v" = 5/30`
v = `30/5`
v = 6 cm
The positive value of v indicates that the image is formed behind the mirror. The positive value of magnification indicates that the image formed is virtual and erect.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Find the focal length of a convex mirror whose radius of curvature is 32 cm.
Define the radius of curvature of spherical mirrors.
State the relation between object distance, image distance and focal length of a spherical mirror (concave mirror or convex mirror).
What kind of mirrors are used in big shopping centres to watch the activities of the customers?
Where would the image be formed by a convex mirror if the object is placed:
between infinity and pole of the mirror?
Draw labelled ray-diagrams to show the formation of image in both the case.
A convex mirror used as a rear-view mirror in a car has a radius of curvature of 3 m. If a bus is located at a distance of 5 m from this mirror, find the position of image. What is the nature of the image?
The radius of curvature of a convex mirror used as a rear view mirror in a moving car is 12.0 m. A truck is coming from behind it at a distance of 3.54 m. Calculate (a)
- position and
- size of the image relative to the size of the truck.
- What will be the nature of the image?
Draw ray diagrams to represent the nature, position and relative size of the image formed by a convex lens for the object placed:
at 2F1,
What is the effect on the size and position of the image of moving the object (i) towards the lens, and (ii) away from the lens?
The magnification produced by a spherical mirror and a spherical lens is + 0.8.
(a) The mirror and lens are both convex
(b) The mirror and lens are both concave
(c) The mirror is concave but the lens is convex
(d) The mirror is convex but the lens is concave
An object is placed at a distance of 100 cm from each of the above lenses A and B. Calculate (i) image distance, and (ii) magnification, in each of the two cases.
At the point of incidence, a line drawn at right angles to the surface, separating the two media, is called the normal.
The diagram given below in fig shows a ray of light AO falling on a surface separating two media. Draw the refracted ray in each, case.
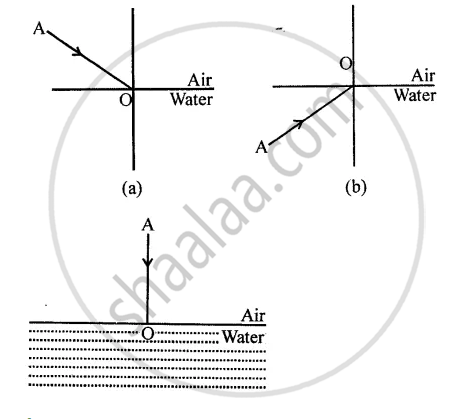
List four properties of the image formed by a convex mirror when object is placed between focus and pole of the mirror.
When the reflecting surface is curved outwards the mirror formed will be ______.
The Convex mirror always forms ______ and ______ image.
Assertion: Convex mirrors are used as a rearview mirror in vehicles for observing traffic at our back.
Reason: A convex mirror has a much larger field of view.
The field of view is maximum for ______.
Match the following.
| Column I | Column II |
| Convex mirror | Radio telescopes |
| Parabolic mirror | Rear-view mirror |
| Snell’s law | Kaleidoscope |
| Dispersion of light | sin i/sin r =μ |
| Refractive index | Rainbow |
