Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
An urn contains 12 red balls, 15 yellow balls and 18 blue balls. A ball is choosen at random, then to find the probability of choosing a blue and red coloured balls, fill in the boxes.
Total number of balls = 12 + `square` + `square` = `square`
(1) Let E be the event that the choosen ball is blue.
Number of blue balls = `square`
Thus,
P(E) = `"Number of blue balls"/"Total number of balls"`
= `square/square`
(2) Let F be the event that the choosen ball is red.
Number of red balls = `square`
Thus,
P(F) = `square/"Total number of balls"`
= `square/square`
Solution
Total number of balls = 12 + 15 + 18 = 45
(1) Let E be the event that the choosen ball is blue.
Number of blue balls = 18
Thus,
P(E) = `"Number of blue balls"/"Total number of balls"`
= `bb18/bb45`
(2) Let F be the event that the choosen ball is red.
Number of red balls = 12
Thus,
P(F) = `bb("Number of red balls")/"Total number of balls"`
= `bb12/bb45`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Choose the correct alternative answer for the following question and write the alphabet.
Which of the following number cannot represent a probability?
Which of the following options shows the highest probability?
A card is drawn from a well shuffled pack of 52 playing cards. Find the probability of the event, the card drawn is a red card.
Activity: Let ‘S’ be the sample space.
∴ n(S) = 52
Event A: Card drawn is a red card.
∴ Total red cards = `square` hearts + 13 diamonds
∴ n(A) = `square`
∴ P(A) = `square/(n("S"))` ......[Formula]
P(A) = `26/52`
P(A) = `square`
If two coins are tossed, find the probability of event getting head on both the coins
If one die is rolled, then find the probability of event that the number on the upper face is greater than 6?
If three coins are tossed simultaneously, find the probability of the event to get no head
A box contains 5 strawberry chocolates, 6 coffee chocolates, and 2 peppermint chocolates. If one of the chocolates is picked from the box at random, find the probability of the following events by completing the activity.
Event A: it is coffee chocolate.
Activity: Let ‘S’ be the sample space.
∴ n(S) = 5 + 6 + 2 = 13
Event A: it is a coffee chocolate.
∴ n(A) = `square`
∴ P(A) = `square/("n"("S"))` .......[Formula]
P (A) = `square/13`
A box contains 36 cards, bearing only one number from 1 to 36 on each. If one card is drawn at random, find the probability of an event that the card drawn bears, a prime number
A box contains 36 cards, bearing only one number from 1 to 36 on each. If one card is drawn at random, find the probability of an event that the card drawn bears, a number divisible by 3
A missing helicopter is reported to have crashed somewhere in the rectangular region shown in the figure. What is the probability that it crashed inside the lake shown in the figure?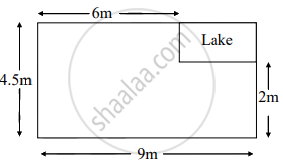
A bag contains 8 red and some blue balls. One ball is drawn at random from the bag. If ratio of probability of getting red ball and blue ball is 2:5, then find the number of blue balls.
In the adjoining figure, the arrow rests on any number, after the rotation of the disc. The probability that it will rest on any of the numbers on the disc is equal. Let A be any random event. To find the probability of A, fill in the boxes.

(1) S = `square`
(2) n(S) = `square`
(3) Let A be the event that arrow points at the number which is perfect cube.
A = `square`
∴ n(A) = `square`
(4) ∴ P(A) = `(n(A))/(n(S)) = square/square = square`
Using the digits 0, 2, 3, 5 the two-digit numbers are constructed without repetition of digits. Find the probability of the following events:
Condition for event A: The number formed is even.
Using the digits 0, 2, 3, 5 the two-digit numbers are constructed without repetition of digits. Find the probability of the following events:
Condition for event B: The number formed is prime number.
Let A be an event. For event A, which probability cannot be possible?
Let E be an event and P(E) = `6/7`, then find the value of P(not E).
From a group of 10 men and 5 women, four member committees are to be formed each of which must contain at least one woman. Then the probability for these committees to have more women than men is ______.
