Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Answer the following.
Explain the screening effect with a suitable example.
Solution
- In a multi-electron atom, the electrons in the inner shells tend to prevent the attractive influence of the nucleus from reaching the outermost electron.
- Thus, they act as a screen or shield between the nuclear attraction and outermost or valence electrons. This effect of the inner electrons on the outer electrons is known as the screening effect or shielding effect.
- Across a period, the screening effect due to inner electrons remains the same as electrons are added to the same shell.
- Down the group, the screening effect due to inner electrons increases as a new valence shell is added.
e.g. Potassium (19K) has electronic configuration 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s1.
K has 4 shells and thus, the valence shell electrons are effectively shielded by the electrons present in the inner three shells. As a result of this, valence shell electron (4s1) in K experiences a much less effective nuclear charge and can be easily removed.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Explain the following.
The atomic radii of Cl, I, and Br are 99, 133, and 114 pm, respectively.
Explain the following.
The ionic radii of FΘ and Na⊕ are 133 and 98 pm, respectively.
Explain the following.
13Al is a metal, 14Si is a metalloid and 15P is a nonmetal.
Answer the following.
Ionization enthalpy of Li is 520 kJ mol-1 while that of F is 1681 kJ mol-1. Explain.
Answer the following.
Why the second ionization enthalpy is greater than the first ionization enthalpy?
Choose the correct option.
Consider the elements B, Al, Mg, and K predict the correct order of metallic character:
Choose the correct option.
The lanthanides are placed in the periodic table at
Answer the following question.
Select the smaller ion form the following pair:
K+, Li+
Answer the following question.
Select the smaller ion form the following pair:
N3–, F–
With the help of a diagram answer the questions are given below:
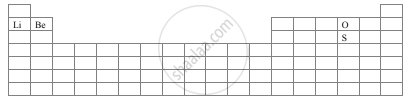
- Which atom should have smaller ionization energy, oxygen, or sulphur?
- The lithium forms +1 ions while beryllium forms +2 ions?
Define ionic radius
Define electronegativity
What are the valence electrons?
Define ionization enthalpy.
How does ionization enthalpy vary down the group and across a period?
How the atomic size vary in a group and across a period? Explain with suitable example.
Give reason.
Inert gases have exceptionally high ionization enthalpies.
Give reason.
Fluorine has less electron affinity than chlorine.
Give reason.
Noble gases possess relatively large atomic size.
