Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Answer the following question.
Differentiate between incomplete dominance and co-dominance. Substantiate your answer with one example of each.
Solution
Co-dominance is the phenomenon in which both the alleles of a contrasting character are expressed in the heterozygous condition. Both the alleles of a gene are equally dominant. ABO blood group in human beings is an example of co-dominance. The blood group character is controlled by three sets of alleles, namely 3 4. The alleles, AB I and I, are equally dominant and are said to be co-dominant as they are expressed in the AB blood group. Both these alleles do not interfere with the expression of each other and produce their respective antigens. Hence, the AB blood group is an example of co-dominance.
| Allele from Parent1 | Allele from Parent2 | Genotype of offspring | Blood type of offspring |
| |A | |A | |A |A | A |
| |A | |B | |A|B | AB |
| |A | i | |Ai | A |
| |B | |A | |A |B | AB |
| |B | |B | |B |B | B |
| |B | i | |B i | B |
| i | i | i i | O |
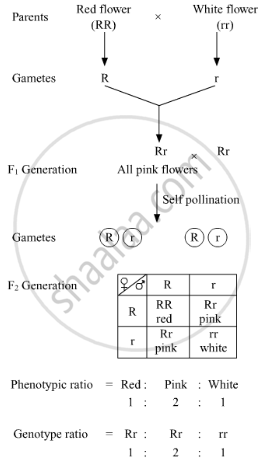
Incomplete dominance is a phenomenon in which one allele shows incomplete dominance over the other member of the allelic pair for a character. For example, a monohybrid cross between the plants having red flowers and white flowers in Antirrhinum species will result in all pink flower plants in the F1 generation. The progeny obtained in F1 generation does not resemble either of the parents and exhibits intermediate characteristics. This is because the dominant allele, R, is partially dominant over the other allele, r. Therefore, the recessive allele, r, also gets expressed in the F1 generation resulting in the production of intermediate pink flowering progenies with Rr genotype.
RELATED QUESTIONS
In humans, the dominance relationship between the A and B alleles of the ABO blood group gene is an example of ______.
A man with blood group 'A' marries a woman with blood group 'B'. What are all the possible blood groups of their offsprings?
Multiple alleles control inheritance of ______.
Alleles that produce independent effects in their heterozygous condition are called ______.
The number of phenotypes in ABO blood groups is ______.
Mother and father of a person with ‘O’ blood group have ‘A’ and ‘B’ blood group respectively. What would be the genotype of both mother and father?
What can be the blood group of offspring when both parents have AB blood group?
Inheritance of roan coat in cattle is an example of ______.
In mice, Y is the dominant allele for yellow fur and y is the recessive allele for grey fur. Since Y is lethal when homozygous, the result of cross Yy × Yy will be ______.
When both alleles express their effect on being present together, the phenomenon is called:
Discuss the genetic basis of wrinkled phenotype of pea seed.
With the help of an example differentiate between incomplete dominance and co-dominance.
In shorthorn cattle, the coat colours red or white are controlled by a single pair of alleles. A calf which receives the allele for red coat from its mother and the allele for white coat from its father is called a 'roan'. It has an equal number of red and white hairs in its coat.
- Is this an example of codominance or of incomplete dominance?
- Give a reason for your answer.
- With the help of genetic cross explain what will be the consequent phenotype of the calf when,
- red is dominant over white.
- red is incompletely dominant.
