Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Answer the following question.
What is a conical pendulum?
Solution
In a simple pendulum, a mass m is suspended by a string of length l and moves along an arc of a vertical circle. If the mass instead revolves in a horizontal circle and the string which makes a constant angle with the vertical describes a cone whose vertex is the fixed point O, then the mass string system is called a conical pendulum.
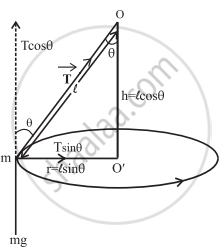
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
For a particle performing uniform circular motion `vecv=vecomegaxxvecr`obtain an expression for linear acceleration of the particle performing non-uniform circular motion.
An aircraft executes a horizontal loop of radius 1.00 km with a steady speed of 900 km/h. Compare its centripetal acceleration with the acceleration due to gravity.
Read the statement below carefully and state, with reason, if it is true or false:
The acceleration vector of a particle in uniform circular motion averaged over one cycle is a null vector.
Why is the motion of a body moving with a constant speed around a circular path said to be accelerated?
Give an example of motion in which speed remains uniform, but the velocity changes.
A uniform circular motion is an accelerated motion. Explain it. State whether the acceleration is uniform or variable? Name the force responsible to cause this acceleration. What is the direction of force at any instant? Draw a diagram in support of your answer.
| A small pebble tied at one end of a string is placed near the periphery of a circular disc, at the centre of which the other end of the string is tied to a peg. The disc is rotating about an axis passing through its centre. |
- What will be your observation when you are standing outside the disc? Explain.
- What will be your observation when you are standing at the centre of the disc? Explain.
State True or False
The earth moves around the sun with a uniform.
Which of the following remains constant in a uniform circular motion, Speed or Velocity, or both?
Name the force required for uniform circular motion. State its direction.
A particle goes round a circular path with uniform speed v. After describing half the circle, what is the change in its centripetal acceleration?
A particle is moving in uniform circular motion with speed 'V' and radius 'R'. The angular acceleration of the particle is ______.
A disc has mass 'M' and radius 'R'. How much tangential force should be applied to the rim of the disc, so as to rotate with angular velocity 'ω' in time t?
Consider a simple pendulum of length 4 m. Its bob performs a circular motion in horizontal plane with its string making an angle 60° with the vertical. The Period of rotation of the bob is ____________.(Take g = 10 m/s2)
A wheel is 0.25 m in radius. When it makes 15 revolutions per minute, its linear speed at the point on circumference is ____________.
At any instant, the magnitude of the centripetal force on a particle of mass 'm' performing circular motion is given by (ω = angular velocity and v = linear velocity of the particle) ______.
A mass 'm' is tied to one end of a spring and whirled in a horizontal circle with constant angular velocity. The elongation in the spring is 1 cm. If the angular speed is doubled, the elongation in the spring is 6 cm. The original length of the spring is ______.
Two particles P and Q are moving in concentric circles of rarui rp and rQ respectively. If their period of revolutions are in ratio 2 : 3, then ratio of their centripetal acceleration is ____________.
A cyclist is riding with a speed of 43.2 km/h. As he approaches a circular turn on the road of radius 60 m, he applies brakes and reduces his speed at constant rate of 1.8 ms-2. The magnitude of the net acceleration of the cyclist is ______.
The given graph represents motion with ______ speed.
The motion of the bus is ______ motion.
For a particle performing uniform circular motion, choose the correct statement(s) from the following:
- Magnitude of particle velocity (speed) remains constant.
- Particle velocity remains directed perpendicular to radius vector.
- Direction of acceleration keeps changing as particle moves.
- Angular momentum is constant in magnitude but direction keeps changing.
A particle moves along a circle of radius r with constant tangential acceleration. If the velocity of the particle is v at the end of second revolution, after the revolution has started, then the tangential acceleration is ______.
Angular speed of hour hand of a clock in degree per second is ______.
A wheel is rotating at 900 rpm about its axis. When the power is cut off it comes to rest in 1 min. The angular retardation (assumed to be uniform (in rad s-1) is ______.
Why is uniform circular motion said to be accelerated?
