Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
An electron beam projected along the positive x-axis deflects along the positive y-axis. If this deflection is caused by a magnetic field, what is the direction of the field? Can we conclude that the field is parallel to the z-axis?
Solution
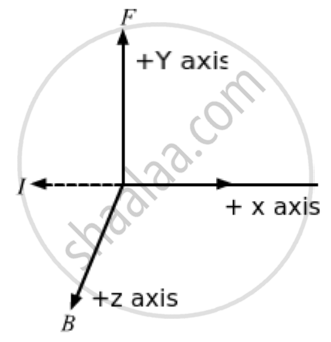
As the particle gets deflected towards the positive y-axis, we can conclude that force is acting on the particle along the positive y-axis. Now, as the electron is moving along the positive x-axis, the current can be assumed to be flowing along the negative x-axis. Applying Fleming's left-hand rule, we find that the thumb points in the direction of force, i.e. the positive y-axis and the middle finger points in the direction of current, i.e. negative x-axis. Consequently, the forefinger gives us the direction of magnetic field, i.e. out of the plane of the paper or in the positive z-direction. So, we can conclude that the magnetic field is pointing along the positive z-axis.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Using the concept of force between two infinitely long parallel current carrying conductors, define one ampere of current.
What is the magnitude of magnetic force per unit length on a wire carrying a current of 8 A and making an angle of 30° with the direction of a uniform magnetic field of 0.15 T?
A long, straight wire of radius R carries a current distributed uniformly over its cross section. T he magnitude of the magnetic field is
(a) maximum at the axis of the wire
(b) minimum at the axis of the wire
(c) maximum at the surface of the wire
(d) minimum at the surface of the wire.
A current of 10 A is established in a long wire along the positive z-axis. Find the magnetic field \[\vec{B}\] at the point (1 m, 0, 0).
A copper wire of diameter 1.6 mm carries a current of 20 A. Find the maximum magnitude of the magnetic field `vecB` due to this current.
A transmission wire carries a current of 100 A. What would be the magnetic field B at a point on the road if the wire is 8 m above the road?
A rectangular coil of 100 turns has length 5 cm and width 4 cm. It is placed with its plane parallel to a uniform magnetic field and a current of 2 A is sent through the coil. Find the magnitude of the magnetic field B if the torque acting on the coil is 0.2 N m−1
A long, straight wire carries a current i. Let B1 be the magnetic field at a point P at a distance d from the wire. Consider a section of length l of this wire such that the point P lies on a perpendicular bisector of the section B2 be the magnetic field at this point due to this second only. Find the value of d/l so that B2 differs from B1 by 1%.
Three coplanar parallel wires, each carrying a current of 10 A along the same direction, are placed with a separation 5.0 cm between the consecutive ones. Find the magnitude of the magnetic force per unit length acting on the wires.
Two parallel wires separated by a distance of 10 cm carry currents of 10 A and 40 A along the same direction. Where should a third current by placed so that it experiences no magnetic force?
A conducting circular loop of radius a is connected to two long, straight wires. The straight wires carry a current i as shown in figure. Find the magnetic field B at the centre of the loop.
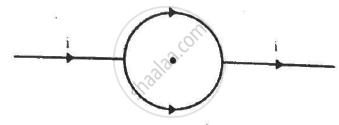
If a current I is flowing in a straight wire parallel to x-axis and magnetic field is there in the y-axis then, ______.
Three infinitely long parallel straight current-carrying wires A, B and C are kept at equal distance from each other as shown in the figure. The wire C experiences net force F. The net force on wire C, when the current in wire A is reversed will be ______.
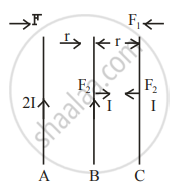
Equal currents are passing through two very long and straight parallel wires in the same direction. They will ______
Five long wires A, B, C, D and E, each carrying current I are arranged to form edges of a pentagonal prism as shown in figure. Each carries current out of the plane of paper.
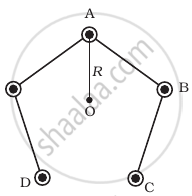
- What will be magnetic induction at a point on the axis O? AxisE is at a distance R from each wire.
- What will be the field if current in one of the wires (say A) is switched off?
- What if current in one of the wire (say) A is reversed?
Two long straight parallel conductors carrying currents I1 and I2 are separated by a distance d. If the currents are flowing in the same direction, show how the magnetic field produced by one exerts an attractive force on the other. Obtain the expression for this force and hence define 1 ampere.
Two long parallel wires kept 2 m apart carry 3A current each, in the same direction. The force per unit length on one wire due to the other is ______.
Two long straight parallel current-carrying conductors are kept ‘a’ distant apart in the air. The direction of current in both the conductors is the same. Find the magnitude of force per unit length and the direction of the force between them. Hence define one ampere.
The figure below are two long, parallel wires carrying current in the same direction such that I1 < I2.
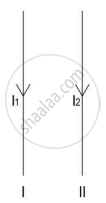
- In which direction will wire I1 move?
- If the direction of the current I2 is reversed, in which direction will the wire I1 move now?
