Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Assuming temperature remaining constant calculate the pressure of the gas in the following:
The pressure of a gas having volume 100 lits. originally occupying 75 dm3 at 700 mm. pressure.
Solution
P1 = 700 mm
V1 = 75 dm3
P2 = ?
V2 = 100 lits But 1 dm3 = 1 litre
∴ V2 = 100 dm3
At constant temperature P1V1 = P2V2
∴ P2 = `("P"_1"V"_1)/"V"_2 = (700 xx 75)/100 = 525` mm
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
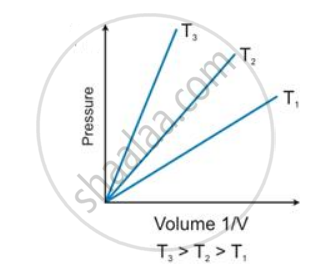
State the law which is represented by the following graph:
A gas at 240 K is heated to 127°C. Find the percentage change in the volume of the gas (pressure remaining constant).
Calculate the volume occupied by 2 g of hydrogen at 27°C and 4-atmosphere pressure if at STP it occupies 22.4 litres.
Calculate the volume of dry air at STP that occupies 28 cm3 at 14°C and 750 mmHg pressure when saturated with water vapour. The vapour pressure of water at 14°C is 12 mmHg.
Give its
(i) mathematical expression
(ii) graphical representation and
(iii) significance.
50 cm3 of hydrogen is collected over water at 17°C and 750 mmHg pressure. Calculate the volume of a dry gas at STP. The water vapour pressure at 17°C is 14 mmHg.
Calculate the volume of a gas ‘A’ at s.t.p., if at 37°C and 775 mm of mercury pressure, it occupies a volume of `9 1/2` litres.
Calculate the following:
A gas ‘X’ is collected over water at 17°C and 750 mm. pressure. If the volume of the gas collected is 50 cc., calculate the volume of the dry gas at s.t.p. [at 17°C the vapour pressure is 14 mm.]
Assuming temperature remaining constant calculate the pressure of the gas in the following:
The pressure of a gas having volume 1000 cc. originally occupying 1500 cc. at 720 mm. pressure.
Assuming temperature remaining constant calculate the pressure of the gas in the following:
The pressure of a gas having volume 1800 ml. originally occupying 300 ml. at 6 atms. pressure.
