Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
50 cm3 of hydrogen is collected over water at 17°C and 750 mmHg pressure. Calculate the volume of a dry gas at STP. The water vapour pressure at 17°C is 14 mmHg.
Solution
V = 50 cm3
P = 750 - 14 = 736 mm
T = 290 K
P1 = 760 mm
V1= ?
T1 = 273 K
Using gas equation,
`("P" "V")/"T" = ("P"_1 "V"_1)/"T"_1`
`(736 xx 50)/290 = (760 xx "V"_1)/273`
`"V"_1 = 45.6 "cm"^3`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Explain Boyle's Law on the basis of the kinetic theory of matter.
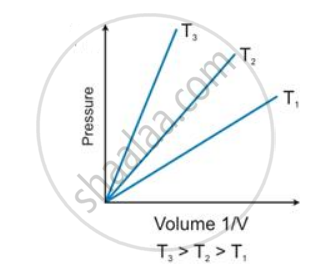
State the law which is represented by the following graph:
At 0°C and 760 mmHg pressure, a gas occupies a volume of 100 cm3. Kelvin temperature of the gas is increased by one-fifth and the pressure is increased one and a half times. Calculate the final volume of the gas.
Calculate the volume occupied by 2 g of hydrogen at 27°C and 4-atmosphere pressure if at STP it occupies 22.4 litres.
Calculate the volume of dry air at STP that occupies 28 cm3 at 14°C and 750 mmHg pressure when saturated with water vapour. The vapour pressure of water at 14°C is 12 mmHg.
Name or state the following:
The law which studies the relationship between pressure of a gas and the volume occupied by it at constant temperature.
Calculate the following:
Calculate the temperature at which a gas ‘A’ at 20°C having a volume, of 500 cc. will occupy a volume of 250 cc.
Fill in the blank with the correct word, from the words in option:
1 dm3 of a gas is equal to _______.
State Boyle’s law
State-the law of volume
