Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Can you recall meiosis and indicate at what stage a recombinant DNA is made?
Solution
In meiosis, the number of chromosomes is reduced to half. In the first meiotic division, one or more segments are exchanged between homologous chromosomes of each pair, i.e., they cross over.
Homologous chromosomes form pairs in the zygotene substage of the first prophase of meiotic division. This process is called synapsis. In the pachytene substage, round microscopic knobs appear at one or more places in the synaptonemal complex, these are called recombination nodules.
The mutual exchange of one or more segments between the interconnected chromatids of homologous chromosomes is called crossing over. This results in the formation of homologous recombinant DNA. Recombination nodes are formed at the sites where pieces of chromatids break and rejoin for transduction.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Name two commonly used bioreactors.
Can you list 10 recombinant proteins which are used in medical practice? Find out where they are used as therapeutics (use the internet).
Besides better aeration and mixing properties, what other advantages do stirred tank bioreactors have over shake flasks?
Describe briefly the following:
Downstream processing
Explain briefly:
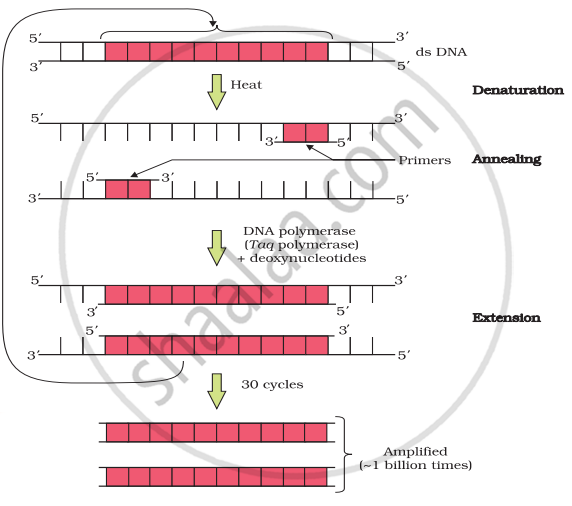
PCR
Prepare a flow chart in formation of recombinant DNA by the action of restriction endonuclease enzyme EcoRI.
PCR and restriction fragment length polymorphism are the methods for ______.
PCR proceeds mthree distinct steps governed by temperature, they are in order of ______.
During the purification process for recombinant DNA technology, the addition of chilled ethanol precipitates out ______.
Significance of 'heat shock' method in bacterial transformation is to facilitate ______.
A bacterial cell was transformed with a recombinant DNA molecule that was generated using a human gene. However, the transformed cells did not produce the desired protein. Reasons could be ______.
How is copy number of the plasmid vector related to yield of recombinant protein?
While doing a PCR, ‘denaturation’ step is missed. What will be its effect on the process?
Identify and explain steps ‘A’, ‘B’ and ‘C’ in the PCR diagram given below.
Illustrate the design of a bioreactor. Highlight the difference between a flask in your laboratory and a bioreactor which allows cells to grow in a continuous culture system.
Read the following paragraph and answer the questions that follow:
| Biotechnology revolves around the "gene of interest", with an objective to open various avenues for human welfare in health, medicine, pharma, agriculture etc. using different techniques, tools and processes. One of the breakthroughs of biotechnology in medicine is the gene therapy. |
- Name the human disease for which the gene therapy was used for the first time.
- Explain the steps of gene therapy carried to cure the disease using the lymphocytes of the patient. Why is this therapy not a permanent cure of the disease?
- Write the possible permanent cure of the disease by the gene therapy that is in progress.
Write the scientific name of the source organism of the thermostable DNA polymerase used in PCR.
