Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Answer the following question:
Carbon cannot reduce the oxides of sodium, magnesium, and aluminum to their respective metals. Why? Where are these metals placed in the reactivity series? How are these metals obtained from their ores? Take an example to explain the process of extraction along with chemical equations.
Solution
Oxides of sodium, magnesium and aluminium are very strong oxides as these metal are very reactive metals, but carbon is not a strong reducing agent and hence cannot reduce the reactive metal oxides to metals.
In the reactivity series, sodium, magnesium and aluminium are placed in the upper portion which means these metals are very reactive in nature and carbon is less reactive.
K > Na > Ca > Mg > Al > C > Zn > Fe
Oxides of reactive metals are directly put for electrolytic reduction process to obtain the pure metal.
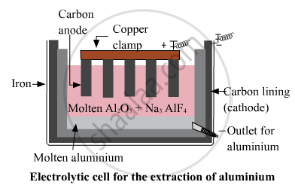
For the oxide of a reactive metal like aluminium oxide, as the metal is already in its oxide state so, it is directly put for the electrolytic reduction process. In this process, graphite electrodes are used as anode and cathode in the electrolytic chamber. The pure aluminium is attracted to the cathode, which is a lining of graphite. The oxygen is attracted to the anode, and bubbles through the solution.
Cathode reaction: at cathode reduction of aluminium takes place and thus aluminium is discharged at the cathode.
\[\ce{Al^3+ + 3e- -> Al}\]
Anode reaction: at anode oxidation takes place and oxygen gas is evolved.
\[\ce{2O^2- -> O2 + 4e-}\]
RELATED QUESTIONS
In the electrolytic refining of a metal M, what would you take as the anode, the cathode and the electrolyte?
Which one of the methods given in column I is applied for the extraction of each of the metals given in column II:
| Column I | Column II |
| Electrolytic reduction | Aluminium |
| Reduction with Carbon | Zinc |
| Reduction with Aluminium | Sodium |
| Iron | |
| Manganese | |
| Tin |
Explain giving one example, how highly reactive metals (which are high up in the reactivity series) are extracted.
State three objectives achieved during the roasting of ores.
Aluminum is used in thermite welding:
write reaction for process?
Define the following term.
Gangue
choose the most appropriate term to match the given description.
Heating of the ore in the absence of air to high temperature
Define roasting.
Find the odd one out and give its explanation.
Which of the following ore is concentrated by the Froth floatation process?
