Advertisements
Advertisements
Questions
Define limiting molar conductivity.
Define the following term:
Limiting molar conductivity (∧°m)
Solution 1
The limiting molar conductivity of an electrolyte is defined as its molar conductivity when the concentration of the electrolyte in the solution approaches zero.
Solution 2
When the concentration of an electrolytic solution placed between electrodes of a conductivity cell placed at a unit distance having an area of cross-section sufficient to accommodate enough volume of solution containing one mole of electrolyte approaches zero, then the conductance of the solution is known as limiting molar conductivity.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The molar conductivity of cation and anion of salt BA are 180 and 220 mhos respectively. The molar conductivity of salt BA at infinite dilution is_____________ .
(a) 90 mhos.cm2
(b) 110 mhos.cm2.mol-1
(c) 200 mhos.cm2.mol-1
(d) 400 mhos.cm2.mol-1
Calculate the degree of dissociation (α) of acetic acid if its molar conductivity (Λm) is 39.05 S cm2 mol−1.
Given λ°(H+) = 349.6 S cm2 mol−1 and λ°(CH3COO−) = 40.9 S cm2 mol−1
When acidulated water (dil.H2SO4 solution) is electrolysed, will the pH of the solution be affected? Justify your answer.
Assertion: Λm for weak electrolytes shows a sharp increase when the electrolytic solution is diluted.
Reason: For weak electrolytes degree of dissociation increases with dilution of solution.
Solutions of two electrolytes ‘A’ and ‘B’ are diluted. The Λm of ‘B’ increases 1.5 times while that of A increases 25 times. Which of the two is a strong electrolyte? Justify your answer. Graphically show the behavior of ‘A’ and ‘B’.
The limiting molar conductivities for Nacl, KBr and KCI are 126, 152 and 150 S cm2 mol–1 respectively. The limiting molar conductivity for Na Br is:-
Given below are two statements:
Statements I: The limiting molar conductivity of KCl (strong electrolyte) is higher compared to that of CH3COOH (weak electrolyte).
Statement II: Molar conductivity decreases with decrease in concentration of electrolyte.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
The solubility of Co2[Fe(CN)6] in water at 25°C from the following data:
Conductivity of saturated solution of Co2[Fe(CN)6] = 2.06 × 10−6 ohm−1 cm−1 and that of water = 4.1 × 10−7 ohm−1 cm−1. The ionic molar conductivities of Co2+ and [Fe(CN)6]4− are 86 and 444 ohm−1 cm2 mol−1 respectively, is ______ × 10−6 mol/L.
The variation of molar conductivity with concentration of an electrolyte (X) m aqueous solution is shown in the given figure.
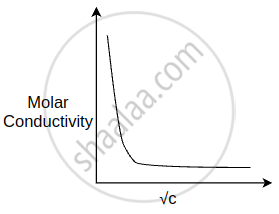
The electrolyte X is ______.
Which of the following solutions will have the highest conductivity at 298 K?
