Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Calculate the degree of dissociation (α) of acetic acid if its molar conductivity (Λm) is 39.05 S cm2 mol−1.
Given λ°(H+) = 349.6 S cm2 mol−1 and λ°(CH3COO−) = 40.9 S cm2 mol−1
Solution
The degree of dissociation of a weak electrolyte is given by the following relation
α = Λm / Λ0 ... Equation (1)
where α is the degree of dissociation of the electrolyte, Λm is the molar conductivity and Λ0 is the molar conductivity at infinite dilution.
We are given that the ionic molar conductivity at infinite dilution of acetate and hydrogen ions are 349.8 and 40.9 S cm2 mol-1 respectively. Hence the limiting molar conductivity of acetic acid would be written as:
Λ0acetic acid = λ0(H+) + λ0(CH3COO-)
= 40.9 + 349.8
= 390.7 cm2 mol-1
Now, since we are given that the molar conductivity of acetic acid is Λm = 39.05 S cm2 mol-1
Therefore, substituting the values in equation (1), we get:
Degree of dissociation of acetic acid = α = Λm/ Λ0 = `39.05/390.7 = 0.0999 " ≅ " 0.1`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Define limiting molar conductivity.
The conductivity of 0.20 mol L−1 solution of KCl is 2.48 × 10−2 S cm−1. Calculate its molar conductivity and degree of dissociation (α). Given λ0 (K+) = 73.5 S cm2 mol−1 and λ0 (C1−) = 76.5 S cm2 mol−1.
Define the following terms: Molar conductivity (⋀m)
Write mathematical expression of molar conductivity of the given solution at infinite dilution.
When acidulated water (dil.H2SO4 solution) is electrolysed, will the pH of the solution be affected? Justify your answer.
Write the cell reaction of a lead storage battery when it is discharged. How does the density of the electrolyte change when the battery is discharged?
Why on dilution the m Λm of \[\ce{CH3COOH}\] increases very fast, while that of \[\ce{CH3COONa}\] increases gradually?
Which of the following halogen acids is the strongest reducing agent?
Molar conductivity of substance “A” is 5.9 × 103 S/m and “B” is 1 × 10–16 S/m. Which of the two is most likely to be copper metal and why?
The variation of molar conductivity with concentration of an electrolyte (X) m aqueous solution is shown in the given figure.
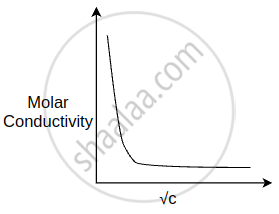
The electrolyte X is ______.
