Commerce (English Medium)
Science (English Medium)
Arts (English Medium)
Academic Year: 2016-2017
Date & Time: 24th March 2017, 12:30 pm
Duration: 3h
Advertisements
Write the formula of an oxo-anion of Manganese (Mn) in which it shows the oxidation state equal to its group number.
Chapter: [0.04] d-block and f-block Elements
Write the IUPAC name of the following compound and classify it as primary, secondary and tertiary amine.
(CH3CH2)2NCH3
Primary
Secondary
Tertiary
Chapter: [0.09] Amines
For a reaction R ---> P, half-life (t1/2) is observed to be independent of the initial concentration of reactants. What is the order of reaction?
Chapter: [0.03] Chemical Kinetics
Write the structure of 1-Bromo-4-chlorobut-2-ene
Chapter: [0.06] Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
Write one similarity between Physisorption and Chemisorption
Chapter: [0.05] Surface Chemistry
Complete the following reactions
NH3+3Cl2(excess) ---->
Chapter: [0.05] Coordination Compounds
Complete the following reactions:
XeF6+2H2O ----->
Chapter: [0.07] P - Block Elements
What happens when (NH4)2Cr2O7 is heated? Write the equations.
Chapter: [0.07] P - Block Elements
What happens when
H3PO3 is heated ?
Write the reactions involved.
Chapter: [0.07] P - Block Elements
Define the term Colligative properties
Chapter: [0.01] Solutions
Draw the structures of the following:
H2S2O7
Chapter: [0.07] P - Block Elements
Draw the structures of the following
XeF6
Chapter: [0.07] P - Block Elements
Calculate the degree of dissociation (α) of acetic acid if its molar conductivity (Λm) is 39.05 S cm2 mol−1.
Given λ°(H+) = 349.6 S cm2 mol−1 and λ°(CH3COO−) = 40.9 S cm2 mol−1
Chapter: [0.02] Electrochemistry
Write the chemical reaction involved in Wolff-Kishner reduction.
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Write the equations involved in the following reactions:
Etard reaction
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Advertisements
A 10% solution (by mass) of sucrose in water has freezing point of 269.15 K. Calculate the freezing point of 10% glucose in water, if freezing point of pure water is 273.15 K
Given : (Molar mass of sucrose = 342 g mol−1)
(Molar mass of glucose = 180 g mol−1)
Chapter: [0.1] Biomolecules
Calculate the mass of Ag deposited at cathode when a current of 2 amperes was passed through a solution of AgNO3 for 15 minutes.
(Given : Molar mass of Ag = 108 g mol−1 lF = 96500 C mol−1)
Chapter: [0.02] Electrochemistry
Define terms: Fuel cell
Chapter: [0.02] Electrochemistry
What type of isomerism is shown by the complex [Co(NH3)6] [Cr(CN)6]?
Chapter: [0.05] Coordination Compounds
Why a solution of [Ni(H2O)6]2+ is green while a solution of [Ni(CN)4]2− is colourless? (At. no. of Ni = 28)
Chapter: [0.05] Coordination Compounds
Write the IUPAC name of the following complex : [Co(NH3)5(CO3)]Cl.
Chapter: [0.05] Coordination Compounds
Write one difference in Lyophobic sol and Lyophilic sol
Chapter: [0.05] Surface Chemistry
Write one difference in Solution and Colloid
Chapter: [0.01] Solutions
Write one difference in Homogeneous catalysis and Heterogeneous catalysis
Chapter: [0.05] Surface Chemistry
Following data are obtained for reaction :
N2O5 → 2NO2 + 1/2O2
| t/s | 0 | 300 | 600 |
| [N2O5]/mol L–1 | 1.6 × 10-2 | 0.8 × 10–2 | 0.4 × 10–2 |
1) Show that it follows first order reaction.
2) Calculate the half-life.
(Given log 2 = 0.3010, log 4 = 0.6021)
Chapter: [0.03] Chemical Kinetics
Following compounds are given to you :
2-Bromopentane, 2-Bromo-2-methylbutane, 1-Bromopentane
1) Write the compound which is most reactive towards SN2 reaction.
2) Write the compound which is optically active.
3) Write the compound which is most reactive towards β-elimination reaction.
Chapter: [0.05] Coordination Compounds
Name the method of refining of metals such as Germanium.
Chapter: [0.06] General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
Out of PbS and PbCO3 (ores of lead), which one is concentrated by froth floatation process preferably?
Chapter: [0.06] General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
What is the significance of leaching in the extraction of aluminium?
Chapter: [0.06] General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
Write structures of compounds A, B and C in of the following reactions
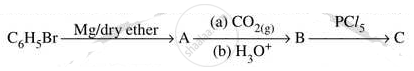
Chapter: [0.05] Coordination Compounds
Write structures of compounds A, B and C in of the following reactions
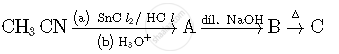
Chapter: [0.05] Coordination Compounds
How will you bring about the following conversion in not more than two steps?
Benzoic acid to Benzaldehyde
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Do the following conversions in not more than two steps :
Ethyl benzene to Benzoic acid
Chapter: [0.09] Amines
Do the following conversions in not more than two steps :
Propanone to Propene
Chapter: [0.09] Amines
Write the names and structures of the monomers of the following polymers: Dacron
Chapter: [0.15] Polymers
Write the structures of the monomers used for getting the following polymers
Melamine – formaldehyde polymer
Chapter: [0.15] Polymers
Write names and chemical formulae of monomers used in preparing Buna-N.
Chapter: [0.15] Polymers
Explain the following terms with suitable examples - Anionic detergents
Chapter: [0.16] Chemistry in Everyday Life
What is meant by the term ‘broad spectrum antibiotics’? Explain.
Chapter: [0.16] Chemistry in Everyday Life
Explain the term Antiseptics
Chapter: [0.16] Chemistry in Everyday Life
Advertisements
Give reasons Thermal stability decreases from H2O to H2Te.
Chapter: [0.07] P - Block Elements
Account for the following : Nitrogen does not form pentahalide.
Chapter: [0.07] P - Block Elements
Give reasons Acetylation of aniline reduces its activation effect.
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Give reasons CH3NH2 is more basic than C6H5NH2.
Chapter: [0.09] Amines
Give reasons Although –NH2 is o/p directing group, yet aniline on nitration gives a significant amount of m-nitroaniline
Chapter: [0.09] Amines
After watching a programme on TV about the presence of carcinogens (cancer causing agents) Potassium bromate and Potassium iodate in bread and other bakery products, Ritu a class XII student decided to aware others about the adverse effects of these carcinogens in foods. She consultanted the school principal and requested him to instruct canteen contractor to stop selling sandwiches, pizza, burgers and other bakery products to the students. Principal took an immediate action and instructed the canteen contractor to replace the bakery products with some proteins and vitamins rich food like fruits, salads, sprouts etc. The decision was welcomed by the parents and students.
After reading the above passage, answer the following questions:
1) What are the values (at least two) displayed by Ritu?
2) Which polysaccharide component of carbohydrates is commonly present in bread?
3) Write the two types of secondary structure of proteins.
4) Give two examples of water soluble vitamins.
Chapter: [0.1] Biomolecules
How would you account for the following: Transition metals form complex compounds.
Chapter: [0.04] d-block and f-block Elements
Give an example and suggest a reason for the following feature of the transition metal chemistry:
The lowest oxide of transition metal is basic, the highest is amphoteric/acidic.
Chapter: [0.04] d-block and f-block Elements
Account for the following:
E° value for the Mn3+/Mn2+ couple is highly positive (+1.57 V) as compare to Cr3+/Cr2+.
Chapter: [0.02] Electrochemistry
Write one similarity and one difference between the chemistry of lanthanoid and actinoid elements.
Chapter: [0.04] d-block and f-block Elements
How is the variability in oxidation states of transition metals different from that of the non-transition metals? Illustrate with examples.
Chapter: [0.04] d-block and f-block Elements
Explain why Cu+ ion is not stable in aqueous solutions?
Chapter: [0.04] d-block and f-block Elements
Orange colour of `Cr_2O_7^(2–)` ion changes to yellow when treated with an alkali. Why?
Chapter: [0.09] Amines
How would you account for the following:
The chemistry of actinoids is more complicated as compared to lanthanoids.
Chapter: [0.04] d-block and f-block Elements
An element has atomic mass 93 g mol–1 and density 11.5 g cm–3. If the edge length of its unit cell is 300 pm, identify the type of unit cell
Chapter: [0.01] Solid State
Write any two differences between amorphous solids and crystalline solids
Chapter: [0.01] Solid State
Calculate the number of unit cells in 8.1 g of aluminium if it crystallizes in a f.c.c. structure. (Atomic mass of Al = 27 g mol–1)
Chapter: [0.01] Solid State
Give reasons : In stoichiometric defects, NaCl exhibits Schottky defect and not Frenkel defect.
Chapter: [0.01] Solid State
Give reasons : Silicon on doping with Phosphorous forms n-type semiconductor.
Chapter: [0.01] Solid State
Give reasons:Ferrimagnetic substances show better magnetism than antiferromagnetic substances.
Chapter: [0.01] Solid State
Write the product(s) in the following reactions

Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Write the product(s) in the following reactions
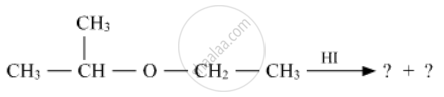
Chapter: [0.07] Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
Write the product(s) in the following reaction
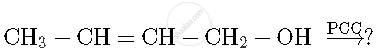
Chapter: [0.07] Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds :
Ethanol and phenol
Chapter: [0.07] Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds :
Propanol and 2-methylpropan-2-ol
Chapter: [0.07] Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
Write the formula of reagents used in the following reactions :
Bromination of phenol to 2,4,6-tribromophenol
Chapter: [0.07] Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
Write the formula of reagents used in the following reactions :
Hydroboration of propene and then oxidation to propanol.
Chapter: [0.07] Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
Arrange the following compound groups in the increasing order of their property indicated :
p-nitrophenol, ethanol, phenol (acidic character)
Chapter: [0.05] Coordination Compounds
Arrange the following compound groups in the increasing order of their property indicated :
Propanol, Propane, Propanal (boiling point)
Chapter: [0.05] Coordination Compounds
Write the mechanism (using curved arrow notation) of the following reaction :
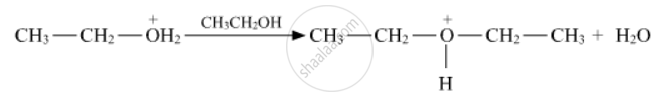
Chapter: [0.07] Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
Other Solutions
Submit Question Paper
Help us maintain new question papers on Shaalaa.com, so we can continue to help studentsonly jpg, png and pdf files
CBSE previous year question papers Class 12 Chemistry with solutions 2016 - 2017
Previous year Question paper for CBSE Class 12 -2017 is solved by experts. Solved question papers gives you the chance to check yourself after your mock test.
By referring the question paper Solutions for Chemistry, you can scale your preparation level and work on your weak areas. It will also help the candidates in developing the time-management skills. Practice makes perfect, and there is no better way to practice than to attempt previous year question paper solutions of CBSE Class 12.
How CBSE Class 12 Question Paper solutions Help Students ?
• Question paper solutions for Chemistry will helps students to prepare for exam.
• Question paper with answer will boost students confidence in exam time and also give you an idea About the important questions and topics to be prepared for the board exam.
• For finding solution of question papers no need to refer so multiple sources like textbook or guides.
