Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Following data are obtained for reaction :
N2O5 → 2NO2 + 1/2O2
| t/s | 0 | 300 | 600 |
| [N2O5]/mol L–1 | 1.6 × 10-2 | 0.8 × 10–2 | 0.4 × 10–2 |
1) Show that it follows first order reaction.
2) Calculate the half-life.
(Given log 2 = 0.3010, log 4 = 0.6021)
Solution
1) For 1st order reaction the integral rate law is :
kt = `ln a_0/a_t`
Given
a0 = 1.6×10−2 mol L−1
For t = 300 s, at = 0.8×10−2 mol L−1
For t = 600 s, at = 0.4×10−2 mol L−1
Using first set of data in the rate law,
`k xx 300 = ln (1.6 xx 10^(-2))/(0.8xx 10^(-2))`
k = `0.00231 s^(-1)`
Using second set of data in the rate law,
`k xx 600 = ln (1.6 xx 10^(-2))/(0.4 xx 10^(-2))`
k = 0.00231 s-1
The value of k is consistent, therefore it follows first order reaction.
2) The half life of first order reaction is given by the following equation:
`t_(1/2) = (ln 2)/k = 2.303 xx (log 2)/k`
`:. t_(1/2) = 2.303 xx (log 2)/0.00231 = 300.08 s`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The time required for 10% completion of a first order reaction at 298 K is equal to that required for its 25% completion at 308 K. If the value of A is 4 × 1010 s−1. Calculate k at 318 K and Ea.
A first order reaction takes 20 minutes for 25% decomposition. Calculate the time when 75% of the reaction will be completed.
(Given : log = 2 = 0·3010, log 3 = 0·4771, log 4 = 0·6021)
Define order of reaction. How does order of a reaction differ from molecularity for a complex reaction?
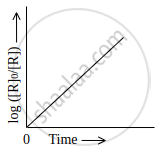
Which of the following graphs is correct for a first order reaction?

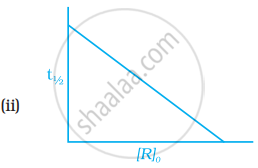
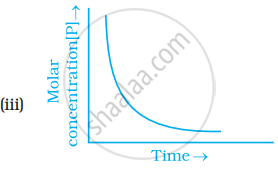
First order reaction is 50% complete in 1.26 × 1014s. How much time could it take for 100% completion?
A first order reaction is 50% complete in 20 minute What is rate constant?
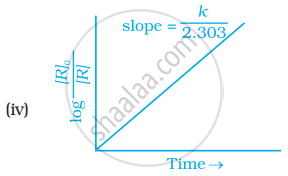
Observe the graph shown in figure and answer the following questions:
- What is the order of the reaction?
- What is the slope of the curve?
- Write the relationship between k and t1/2 (half life period).
The slope in the plot of ln[R] vs. time for a first order reaction is ______.
What is the rate constant?
Write the unit of rate constant [k] for the first order reaction.
