Advertisements
Advertisements
Questions
Give an example and suggest a reason for the following feature of the transition metal chemistry:
The lowest oxide of transition metal is basic, the highest is amphoteric/acidic.
Account for the following:
The lowest oxide of transition metal is basic whereas the highest oxide is amphoteric or acidic.
Account for the following:
The lowest oxide of transition metal is basic, and the highest is acidic.
Solution 1
The lowest oxide has the lowest oxidation state of the transition metal. Hence, the oxide is basic and tends to react with acids to get oxidised to attain a higher oxidation state. Whereas the highest oxides are formed in higher oxidation states. As a result, these oxides are amphoteric acidic. For example, \[\ce{MnO}\] is basic, whereas \[\ce{Mn2O7}\] is acidic.
Solution 2
In the case of a lower oxide of a transition metal, the metal atom has some electrons present in the valence shell of the metal atom that are not involved in bonding. As a result, it can donate electrons and behave as a base, whereas in the higher oxide of a transition metal, the metal atom does not have an electron in the valence shell for donation. As a result, it can accept electrons and behave as an acid.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Complete the following equations:
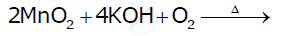
Complete the following equation:
\[\ce{2MnO4- + 6H+ + 5NO2- ->}\]
Complete the following chemical equation
8MnO4- + 3S2O32- + H2O →
Complete the following equations : MnO4- + 4H+ + 3e- →
Give an example and suggest a reason for the following feature of the transition metal chemistry:
A transition metal exhibits the highest oxidation state in oxides and fluorides.
Complete the following equation :
Name a member of the lanthanoid series that is well-known to exhibit +2 oxidation state.
E0 value for Mn3+ Mn2+ couple is much more positive than that for Cr3-/ Cr2-.
Write the chemical equation for the preparation of 4 KMnO from 2. MnO Why does purple colour of acidified permanganate solution decolourise when it oxidises Fe2- to Fe3+ ?
Which of the following reactions are disproportionation reactions?
(a) \[\ce{Cu^{+} -> Cu^{2+} + Cu}\]
(b) \[\ce{3MnO^{-}4 + 4H^{+} -> 2MnO^{-}4 + MnO2 + 2H2O}\]
(c) \[\ce{2KMnO4 -> K2MnO4 + MnO2 + O2}\]
(d) \[\ce{2MnO^{-}4 + 3Mn^{2+} + 2H2O -> 5MnO2 + 4H^{+}}\]
Which of the following is amphoteric oxide?
\[\ce{Mn2O7, CrO3, Cr2O3, CrO, V2O5, V2O4}\]
When orange solution containing \[\ce{Cr2O^{2-}7}\] ion is treated with an alkali, a yellow solution is formed and when \[\ce{H^+}\] ions are added to yellow solution, an orange solution is obtained. Explain why does this happen?
Potassium permanganate acts as an oxidant in neutral, alkaline as well as acidic media. The final products obtained from it in the three conditions are, respectively.
KMnO4 is coloured due to ______.
The oxidation state of manganese in the product obtained in a reaction of potassium permanganate and hydrogen peroxide in a basic medium is ______.
Complete the reaction mentioning all the products formed:
\[\ce{Cr2O^{2-}7 + 3H2S + 8H^+ ->}\]
Indicate the steps in the preparation of \[\ce{K2Cr2O7}\] from chomite ore.
Indicate the steps in the preparation of \[\ce{K2Cr2O7}\] from chromite ore.
Indicate the steps in the preparation of \[\ce{K2Cr2O7}\] from chromite ore.
