Science (English Medium)
Academic Year: 2024-2025
Date: March 2025
Advertisements
GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS:
Read the following instructions carefully.
- There are 33 questions in this question paper with internal choice.
- SECTION A consists of 16 multiple-choice questions carrying 1 mark each.
- SECTION B consists of 5 short answer questions carrying 2 marks each.
- SECTION C consists of 7 short answer questions carrying 3 marks each.
- SECTION D consists of 2 case-based questions carrying 4 marks each.
- SECTION E consists of 3 long answer questions carrying 5 marks each.
- All questions are compulsory.
- Use of log tables and calculators is not allowed.
Ammonolysis of ethyl chloride followed by reaction of the amine so formed with 1 mole of methyl chloride gives an amine that ______.
reacts with Hinsberg reagent to form a product soluble in an alkali.
on reaction with Nitrous acid, produced nitrogen gas.
reacts with Benzenesulphonyl chloride to form a product that is insoluble in alkali.
does not react with Hinsberg reagent.
Chapter:
Which one of the following has the highest dipole moment?
\[\ce{CH3F}\]
\[\ce{CH3Cl}\]
\[\ce{CH3I}\]
\[\ce{CH3Br}\]
Chapter:
Match the properties given in column I with the metals in column II:
| Column I | Column II | ||
| (i) | Actinoid having configuration [Rn] 5f76d17s2 | (A) | Ce |
| (ii) | Lanthanoid, which has a 4f14 electronic configuration in +3 oxidation state. | (B) | Lu |
| (iii) | Lanthanoid, which show +4 Oxidation state | (C) | Cm |
(i) - (C), (ii) - (B), (iii) - (A)
(i) - (C), (ii) - (A), (iii) - (B)
(i) - (A), (ii) - (B), (iii) - (C)
(i) - (B), (ii) - (A), (iii) - (C)
Chapter:
Study the graph showing the boiling points of bromoalkanes and identify the compounds.
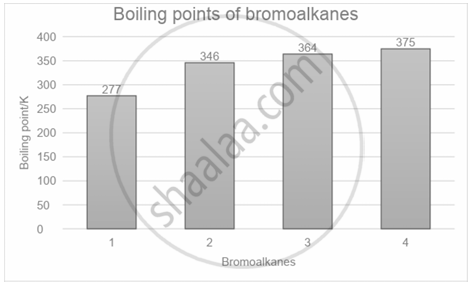
1 = Bromomethane, 2 = 2-Bromobutane, 3 = 1-Bromobutane, 4 = 2-Bromo-2-methylpropane
1 = 1-Bromobutane, 2 = 2-Bromo-2-methylpropane, 3 = 2-Bromobutane, 4 = Bromomethane
1 = Bromomethane, 2 = 1-Bromobutane, 3 = 2-Bromo-2-methylpropane, 4 = 2-Bromobutane
1 = Bromomethane, 2 = 2-Bromo-2-methylpropane, 3 = 2-Bromobutane, 4 = 1-Bromobutane
Chapter:
The initial concentration of R in the reaction \[\ce{R -> P}\] is 4.62 × 10-2 mol/L. What is the half life for the reaction if k = 2.31 × 10-2 mol L-1 s-1?
30 s
3 s
1 s
10 s
Chapter:
When \[\ce{C6H5COOCOCH3}\] is treated with \[\ce{H2O}\], the product obtained is ______.
Benzoic acid and ethanol
Benzoic acid and ethanoic acid
Acetic Acid and phenol
Benzoic anhydride and methanol
Chapter:
| Formulation of Cobalt (III) Chloride-Ammonia Complexes | ||
| Colour | Formula | Solution conductivity corresponds to |
| Yellow | \[\ce{[Co(NH3)6]^{3+} 3Cl−}\] | Y |
| Purple | \[\ce{[CoCl(NH3)5]^{2+} 2Cl^-}\] | 1 : 2 electrolyte |
| Green | X | 1 : 1 electrolyte |
‘X’ and ‘Y’ in the above table are:
X = \[\ce{[Co(NH3)6]^{2+} 3Cl−}\], Y = 1 : 3
X = \[\ce{[Co(NH3)4Cl2]+Cl-}\], Y = 1 : 3
X = \[\ce{[Co(NH3)4Cl2]+Cl−}\], Y = 1 : 1
X = \[\ce{[Co(NH3)4Cl2]^{3+} 3Cl−}\], Y = 1 : 1
Chapter:
Which of the following contains only β-D-glucose as its monosaccharide unit?
Sucrose
Cellulose
Starch
Maltose
Chapter:
Which one of the following sets correctly represents the increase in the paramagnetic property of the ions?
\[\ce{Ti^{3+} < Fe^{2+} < Cr^{3+} < Mn^{2+}}\]
\[\ce{Ti^{3+} < Mn^{2+} < Fe^{2+} < Cr^{3+}}\]
\[\ce{Mn^{2+} < Fe^{2+} < Cr^{3+} < Ti^{3+}}\]
\[\ce{Ti^{3+} < Cr^{3+} < Fe^{2+} < Mn^{2+}}\]
Chapter:
A first-order reaction is found to have a rate constant, k = 5.5 × 10-14 s-1. The time taken for completion of the reaction is:
1.26 × 1013 s
2.52 × 1013 s
0.63 × 1013 s
It never goes to completion.
Chapter:
A student was preparing aniline in the lab. She took a compound “X” and reduced it in the presence of Ni as a catalyst. What could be the compound “X”?
Nitrobenzene
1-Nitrohexane
Benzonitrile
1-Hexanenitrile
Chapter:
Which of the following compound gives an oxime with hydroxylamine:
\[\ce{CH3COCH3}\]
\[\ce{CH3COOH}\]
\[\ce{(CH3CO)2O}\]
\[\ce{CH3COCl}\]
Chapter:
Assertion (A): \[\ce{[Mn(CN)6]^{3−}}\] has a magnetic moment of two unpaired electrons while \[\ce{[MnCl6]^{3−}}\] has a paramagnetic moment of four unpaired electrons.
Reason (R): \[\ce{[Mn(CN)6]^{3−}}\] is an inner orbital complex involving d2sp3 hybridisation; on the other hand, \[\ce{[MnCl6]^{3−}}\] is an outer orbital complex involving sp3d2 hybridisation.
Select the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
A is true but R is false.
A is false but R is true.
Chapter:
Assertion (A): For strong electrolytes, there is a slow increase in molar conductivity with dilution and can be represented by the equation
`wedge_m^circ = wedge_m - A c^(1//2)`
Reason (R): The value of the constant ‘A’ for \[\ce{NaCl}\], \[\ce{CaCl2}\], and \[\ce{MgSO4}\] in a given solvent and at a given temperature is different.
Select the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
A is true but R is false.
A is false but R is true.
Chapter:
Assertion (A): Glucose does not form the hydrogensulphite addition product with \[\ce{NaHSO3}\].
Reason (R): Glucose exists in a six-membered cyclic structure called the pyranose structure.
Select the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
A is true but R is false.
A is false but R is true.
Chapter:
Assertion (A): The half-life for a zero-order reaction is independent of the initial concentration of the reactant.
Reason (R): For a zero-order reaction, Rate = k
Select the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
A is true but R is false.
A is false but R is true.
Chapter:
Nitrogen gas is soluble in water. At temperature 293 K, the value of KH is 76.48 k bar. How would the solubility of nitrogen vary (increase, decrease or remain the same) at a temperature above 293 K if the value of KH rises to 88.8 k bar?
Chapter:
Chloroform (b.p. 61.2°C) and acetone (b.p. 56°C) are mixed to form an azeotrope. The mole fraction of acetone in this mixture is 0.339. Predict whether the boiling point of the azeotrope formed will be
- 60°C
- 64.5°C or
- 54°C
Defend your answer with reason.
Chapter:
A soda bottle will go flat (loose its fizz) faster in Srinagar than in Delhi. Is this statement correct? Why or why not?
Chapter:
How does sugar help in increasing the shelf life of the product?
Chapter:
Write the IUPAC name of the following complex:
\[\ce{K[Cr(H2O)2(C2O4)2]H2O}\]
Chapter:
Advertisements
Name the metal present in the complex compound of Haemoglobin.
Chapter:
Name the metal present in the complex compound of Vitamin B-12.
Chapter:
Observe the following cell and answer the questions that follow:
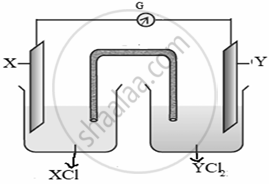
- Represent the cells shown in the figure.
- Name the carriers of the current in the salt bridge.
- Write the reaction taking place at the anode.
Chapter:
Complete the following reaction by writing the major and minor products in the given case.
\[\ce{CH3CH2Br + KCN ->}\]
Chapter:
Complete the following reaction by writing the major and minor products in the given case.
\[\ce{CH3CH2CH = CH2 + HBr ->}\]
Chapter:
Complete the following reaction by writing the major and minor products in the given case.
\[\ce{(CH3)2CHCHClCH3 + alc KOH ->}\]
Chapter:
The presence of carbonyl group in glucose is confirmed by its reaction with hydroxylamine. Identify the type of carbonyl group present and its position. Give a chemical reaction in support of your answer.
Chapter:
Write down the reaction occurring on two inert electrodes when electrolysis of copper chloride is done. What will happen if a concentrated solution of copper sulphate is replaced with copper chloride?
Chapter:
Write an expression for the molar conductivity of aluminium sulphate at infinite dilution according to Kohlrausch law.
Chapter:
Give an example and suggest a reason for the following feature of the transition metal chemistry:
The lowest oxide of transition metal is basic, the highest is amphoteric/acidic.
Chapter: [0.04] d-block and f-block Elements
Account for the following:
Chromium is a hard metal, while mercury is a liquid metal.
Chapter:
Account for the following:
The ionisation energy of elements of the 3d series does not vary much with increasing atomic number.
Chapter:
Give the chemical reaction involved when p-nitrotoluene undergoes the Etard reaction.
Chapter:
Why does Benzoic acid exist as a dimer in an aprotic solvent?
Chapter:
Benzene on reaction with methylchloride in the presence of anhydrous \[\ce{AICI}\], forms toluene. What is the expected outcome if benzene is replaced by benzoic acid? Give a reason for your answer.
Chapter:
An organic compound ‘X’, does not undergo aldol condensation. However, ‘X’ with compound ‘Y’ in the presence of a strong base reacts to give the compound 1, 3-diphenylprop-2-en-1-one.
- Identify 'X’ and Y’.
- Write the chemical reaction involved.
- Give one chemical test to distinguish between X and Y.
Chapter:
Write the structure of all possible dipeptides which can be obtained from glycine and alanine.
Chapter:
Keratin, insulin, and myosin are a few examples of proteins present in the human body. Identify which type of protein is keratin and insulin and differentiate between them based on their physical properties.
Chapter:
Neeta was experimenting in the lab to study the chemical reactivity of alcohol. She carried out a dehydration reaction of propanol at 140°C to 180°C. Different products were obtained at these two temperatures.
- Identify the major product formed at 140°C and the mechanism followed in this case.
- Identify the major product formed at 180°C.
Chapter:
Various isomeric haloalkanes with the general formula \[\ce{C4H9Cl}\] undergo hydrolysis reactions. Among them, compound “A” is the most reactive through SN1 mechanism. Identify “A” citing the reason for your choice. Write the mechanism for the reaction.
Chapter:
Advertisements
The equilibrium constant of a cell reaction:
\[\ce{Sn^{4+}(aq) + Al(s) -> Al^{3+} + Sn^{2+}(aq)}\] is 4.617 × 10184, at 25°C.
- Calculate the standard emf of the cell.
(Given: log 4.617 × 10184 = 184.6644) - What will be the E0 of the half cell \[\ce{Al^{3+}/Al}\], if the E0 of the half cell \[\ce{Sn^{4+}/Sn^{2+}}\] is 0.15 V.
Chapter:
Read the passage carefully and answer the questions that follow.
|
Dependence of the rate of reaction on the concentration of reactants, temperature, and other factors is the most general method for weeding out unsuitable reaction mechanisms. The term mechanism means all the individual collisional or elementary processes involving molecules (atoms, radicals, and ions included) that take place simultaneously or consecutively to produce the observed overall reaction. For example, when hydrogen gas reacts with bromine, the rate of the reaction was found to be proportional to the concentration of \[\ce{H2}\] and to the square root of the concentration of \[\ce{Br2}\]. Furthermore, the rate was inhibited by increasing the concentration of \[\ce{HBr}\] as the reaction proceeded. These observations are not consistent with a mechanism involving bimolecular collisions of a single molecule of each kind. The currently accepted mechanism is considerably more complicated, involving the dissociation of bromine molecules into atoms followed by reactions between atoms and molecules: It is clear from this example that the mechanism cannot be predicted from the overall stoichiometry. |
- Predict the expression for the rate of reaction and order for the following:
\[\ce{H2 + Br2 -> 2HBr}\]
What are the units of rate constant for the above reaction? - How will the rate of reaction be affected if the concentration of \[\ce{Br2}\] is tripled?
OR
What change in the concentration of \[\ce{H2}\] will triple the rate of reaction? - Suppose a reaction between A and B was experimentally found to be first-order with respect to both A and B. So the rate equation is:
Rate = k[A][B]
Which of these two mechanisms is consistent with this experimental finding? Why?
Mechanism 1
\[\ce{A -> C + D (slow)}\]
\[\ce{B + C -> E (fast)}\]
Mechanism 2
\[\ce{A + B -> C + D (slow)}\]
\[\ce{C -> E (fast)}\]
Chapter:
Amines are basic in nature. The pKb value is a measure of the basic strength of an amine. Lower the value of pKb, more basic is the amine. The effect of substituent on the basic strength of amines in aqueous solution was determined using titrations. The substituent “X” replaced \[\ce{^”-CH2^“}\] group in piperidine (compound 1) and propylamine \[\ce{CH3CH2CH2NH2}\], (compound 2).
Compound 1: 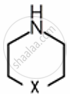
Compound 2: \[\ce{HXCH2CH2NH2}\]
The experimental data is tabulated below:
| Substituent “X” | Electro-negativity of X | Substituted piperidine compound | pKa | Substituted propylamine compound | pKa |
| \[\ce{CH2}\] | 2.55 | 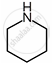 |
11.13 | \[\ce{CH3CH2CH2NH2}\] | 10.67 |
| \[\ce{NH}\] | 3.12 | 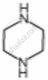 |
9.81 | \[\ce{NH2CH2CH2NH2}\] | 10.08 |
| \[\ce{O}\] | 3.44 | 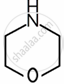 |
8.36 | \[\ce{HOCH2CH2NH2}\] | 9.45 |
| \[\ce{CH3CON}\] | 3.6 | 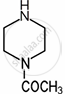 |
7.94 | \[\ce{CH3CONHCH2CH2NH2}\] | 9.28 |
| \[\ce{C6H5CON}\] | 3.7 | 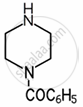 |
7.78 | \[\ce{C6H5CONHCH2CH2NH2}\] | ______ |
Study the above data and answer the following questions:
a. Plot a graph between the electro-negativity of the substituent vs. the pKb value of the corresponding substituted propyl amine (given that pKa + pKb = 14). Is there any relation between the electro-negativity of the substituent and its basic strength?
b. The electronegativity of the substituent \[\ce{^“C6H5CON^“}\] is 3.7; what is the expected pKa value of compound \[\ce{C6H5CONHCH2CH2NH2}\]?
- 9.9
- 9.5
- 9.3
- 9.1
c. The pKa value of the substituted piperidine formed with the substituent “X” is found to be 8.28. What is the expected electronegativity of “X”?
- 3.5
- 3.4
- 3.8
- 3.1
OR
What is the most suitable pKa value of the substituted propylamine formed with substituent “X” with electronegativity 3.0?
- 10.67
- 10.08
- 10.15
- 11.10
Chapter:
- Apurple colour compound A, which is a strong oxidising agent and used for bleaching of wool, cotton, silk and other textile fibres, was added to each of the three test tubes along with \[\ce{H2SO4}\]. It was followed by strong heating.

In which of the above test tubes, A, B or C:
- Violet vapours will be formed.
- The bubbles of gas evolved will extinguish a burning matchstick. Write an equation for each of the above observations.
- A metal ion \[\ce{M^{n+}}\] of the first transition series having d5 configuration combines with three didentate ligands. Assuming Δ0 < P:
- Draw the crystal field energy level diagram for the 3d orbital of this complex.
- What is the hybridisation of \[\ce{M^{n+}}\] in this complex and why?
- Name the type of isomerism exhibited by this complex.
Chapter:
a. Using, Valence Bond Theory identify A, B, C, D, E and F in the following table:
| S. No. | Complex | Central metal in | Configuration of metal ion | Hybridization of Metal ion | Geometry of the Complex | Number Of Unpaired Electron | Magnetic Behaviour |
| i. | \[\ce{[CoF4]^{2-}}\] | \[\ce{A}\] | 3d7 | sp3 | tetrahedral | B | Paramagnetic |
| ii. | \[\ce{[Cr(H2O)2(C2O4)2]}\] | \[\ce{Cr^{3+}}\] | 3d3 | C | octahedral | 3 | D |
| iii. | \[\ce{[Ni(CO)4]}\] | \[\ce{Ni}\] | 3d84s2 | E | F | 0 | Diamagnetic |
b. Write the ionic equations for the reaction of acidified \[\ce{K2Cr2O7}\] with
- \[\ce{H2S}\] and
- \[\ce{FeSO4}\]
Chapter:
Give reasons for the following:
The reaction of ethanol with acetyl chloride is carried out in the presence of pyridine.
Chapter:
Give reasons for the following:
Cresols are less acidic than phenol.
Chapter:
Williamson's process is used for the preparation of ethers from alkyl halide. Identify the alkyl bromide and sodium alkoxide used for the preparation of 2-Ethoxy-3-methylpentane.
Chapter:
Out of formic acid and acetic acid, which one will give the HVZ reaction? Give a suitable reason in support of your answer and write the chemical reaction involved.
Chapter:
Alcohols are acidic but they are weaker acids than water. Arrange various isomers of butanol in the increasing order of their acidic nature. Give a reason for the same.
Chapter:
An organic compound A which is a Grignard reagent is used to obtain 2-methylbutan-2-ol on reaction with a carbonyl compound ‘B’. Identify A’ and ‘B’. Write the equation for the reaction between A and B.
Chapter:
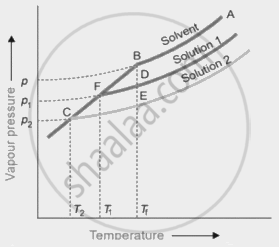
An experiment was carried out in the laboratory to study depression in freezing point. 1 M aqueous solution of \[\ce{Al(NO3)3}\] and 1 M aqueous solution of glucose were taken. From the given figure, identify solution 1 and solution 2. Give a plausible reason for your answer.
Chapter:
The osmotic pressure of a solution of cane sugar was found to be 2.46 atm at 300 K. If the solution was diluted five times, calculate the osmotic pressure at the same temperature.
How can the osmotic pressure of the given cane sugar solution be decreased without changing its volume? Give a reason for your answer.
Chapter:
While giving intravenous injections to the patients, the doctors take utmost care of the concentration of the solution used. Why is it necessary to check the concentration of the solution?
Chapter:
A solution of phenol was obtained by dissolving 2 × 10-2 kg of phenol in 1 kg of benzene. Experimentally, it was found to be 73% associated. Calculate the depression in the freezing point recorded.
Chapter:
Other Solutions
Submit Question Paper
Help us maintain new question papers on Shaalaa.com, so we can continue to help studentsonly jpg, png and pdf files
CBSE previous year question papers Class 12 Chemistry with solutions 2024 - 2025
Previous year Question paper for CBSE Class 12 -2025 is solved by experts. Solved question papers gives you the chance to check yourself after your mock test.
By referring the question paper Solutions for Chemistry, you can scale your preparation level and work on your weak areas. It will also help the candidates in developing the time-management skills. Practice makes perfect, and there is no better way to practice than to attempt previous year question paper solutions of CBSE Class 12.
How CBSE Class 12 Question Paper solutions Help Students ?
• Question paper solutions for Chemistry will helps students to prepare for exam.
• Question paper with answer will boost students confidence in exam time and also give you an idea About the important questions and topics to be prepared for the board exam.
• For finding solution of question papers no need to refer so multiple sources like textbook or guides.
