Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
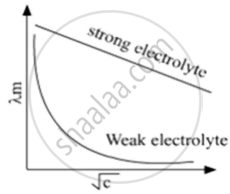
Solutions of two electrolytes ‘A’ and ‘B’ are diluted. The Λm of ‘B’ increases 1.5 times while that of A increases 25 times. Which of the two is a strong electrolyte? Justify your answer. Graphically show the behavior of ‘A’ and ‘B’.
Solution
B is a strong electrolyte. The molar conductivity increases slowly with dilution as there is no increase in number of ions on dilution as strong electrolytes are completely dissociated.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The conductivity of 0.001 mol L-1 solution of CH3COOH is 3.905× 10-5 S cm-1. Calculate its molar conductivity and degree of dissociation (α) Given λ°(H+)= 349.6 S cm2 mol-1 and λ°(CH3COO)= 40.9S cm2mol-1.
Define limiting molar conductivity.
Define the following terms: Molar conductivity (⋀m)
The conductivity of 0.02M AgNO3 at 25°C is 2.428 x 10-3 Ω-1 cm-1. What is its molar
conductivity?
A steady current of 2 amperes was passed through two electrolytic cells X and Y connected in series containing electrolytes FeSO4and ZnSO4 until 2.8g of Fe deposited at the cathode of cell X. How long did the current flow? Calculate the mass of Zn deposited at the cathode of cell Y.
(Molar mass: Fe=56g mol-1,Zn=65.3g mol-1,1F=96500C mol-1)
Which of the statements about solutions of electrolytes is not correct?
\[\ce{Λ^0_m}_{(NH_4OH)}\] is equal to ______.
Which of the following increases with the increase in the concentration of the solution?
Which of the following solutions of KCl will have the highest value of molar conductivity?
The unit of molar conductivity is ______.
