Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Define the term 'focal length of a mirror'.
Solution
The distance between the centre of a lens or curved mirror and its focus.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
What type of wavefront will emerge from a (i) point source, and (ii) distance light source?
A point source of light is placed at a distance of 2 f from a converging lens of focal length f. The intensity on the other side of the lens is maximum at a distance
A particle executes a simple harmonic motion of amplitude 1.0 cm along the principal axis of a convex lens of focal length 12 cm. The mean position of oscillation is at 20 cm from the lens. Find the amplitude of oscillation of the image of the particle.
A converging lens of focal length 15 cm and a converging mirror of focal length 10 cm are placed 50 cm apart. If a pin of length 2.0 cm is placed 30 cm from the lens farther away from the mirror, where will the final image form and what will be the size of the final image?
A 5 mm high pin is placed at a distance of 15 cm from a convex lens of focal length 10 cm. A second lens of focal length 5 cm is placed 40 cm from the first lens and 55 cm from the pin. Find (a) the position of the final image, (b) its nature and (c) its size.
A point object is placed at a distance of 15 cm from a convex lens. The image is formed on the other side at a distance of 30 cm from the lens. When a concave lens is placed in contact with the convex lens, the image shifts away further by 30 cm. Calculate the focal lengths of the two lenses.
Two convex lenses, each of focal length 10 cm, are placed at a separation of 15 cm with their principal axes coinciding. (a) Show that a light beam coming parallel to the principal axis diverges as it comes out of the lens system. (b) Find the location of the virtual image formed by the lens system of an object placed far away. (c) Find the focal length of the equivalent lens. (Note that the sign of the focal length is positive although the lens system actually diverges a parallel beam incident on it.)
A ball is kept at a height h above the surface of a heavy transparent sphere made of a material of refractive index μ. The radius of the sphere is R. At t = 0, the ball is dropped to fall normally on the sphere. Find the speed of the image formed as a function of time for \[t < \sqrt{\frac{2h}{g}}\] . Consider only the image by a single refraction.
A spherical surface of radius R separates two medium of refractive indices µ1 and µ2, as shown in figure. Where should an object be placed in the medium 1 so that a real image is formed in medium 2 at the same distance?
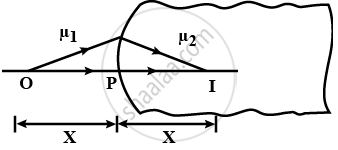
Define the critical angle for a given pair of media and total internal reflection. Obtain the relation between the critical angle and refractive index of the medium.
