Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Derive the equations
(i) v= u+at and
(ii) v2-u2= 2as, where the symbols have their usual meanings.
Solution
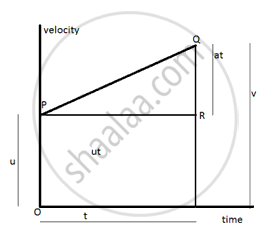
This is graph plotted between velocity and time.
(i) The initial velocity of the body is u at t=O. The velocity of the body increases at a uniform rate and this increase in velocity up to time t is depicted by a straight line PQ. The slope of line PQ gives acceleration a.
a= QR/ PR.
PR= OS =t
SR= OP =u
QR= a x PR.
= a x t .
The point Q corresponds to the final velocity v after time t .
v = QR+ RS and generally we write v = u + at .
This is first equation of motion.
(ii) The area enclosed under a velocity time curve gives the distance covered by a moving body. So total distance S covered by a uniformly accelerating body is given by area of trapezium OSQP.
S = area of trapezium OSQP.
AREA of rectangle OSRP + area of triangle PRQ.
S = OP x OS + 1/2 PR xQR.
s = u x t + 1/2 x t x at .
S= ut + 1/2 at2
This is known as second equation of motion.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A trolley, while going down an inclined plane, has an acceleration of 2 cm s−2. What will be its velocity 3 s after the start?
A racing car has a uniform acceleration of 4 m s−2. What distance will it cover in 10 s after start?
An artificial satellite is moving in a circular orbit of radius 42250 km. Calculate its speed if it takes 24 hours to revolve around the earth.
A body moving with a constant acceleration travels distances 3 m and 8 m, respectively in 1 s and 2 s. Calculate:
- The initial velocity.
- The acceleration of body.
Multiple choice Question. Select the correct option.
A driver applies brakes when he sees a child on the railway track, the speed of the train reduces from 54 km/h to 18 km/h in 5 s. What is the distance travelled by train during this interval of time?
A boy drops a stone from a cliff, reaches the ground in 8 seconds. Calculate
- final velocity of stone
- height of cliff. (Take g = 9.8 ms−2)
A stone thrown vertically upwards takes 4 s to return to the thrower. Calculate
- initial velocity of the stone
- maximum height attained by stone. (Take g = 10 ms−2)
A spaceship is moving in space with a velocity of 50 kms−1. Its engine fires for 10 s, such that its velocity increases to 60 kms−1. Calculate the total distance travelled by a spaceship in 1/2 minute, from the time of firing its engine
A car moving with a uniform acceleration of 10 m/s2 on a straight road changes its speed from 10 m/s to 30 m/s. Find the time lapsed for the change of speed.
A train is moving at a speed of 90 km/h. On applying brakes, a retardation of 2.5 ms-2 is created. At what distance before, should the driver apply the brakes to stop the train at the station?
