Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Describe the mechanism of Nitration of benzene.
Solution
It is prepared by the action of a mixture of con. HNO3 and con. H2SO4 (nitrating mixture) on benzene maintaining the temperature below 333 K.
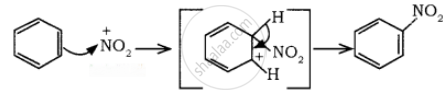
Nitration:

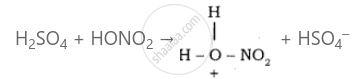
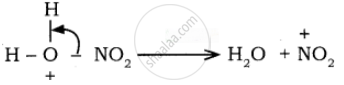
Sulphuric acid generates the electrophile – NO2+, nitronium ion-from nitric acid. This is an example of aromatic electrophilic substitution reaction.
The generation of nitronium ion
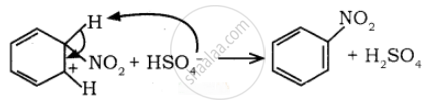
To the nitronium ion (being an electron-deficient species) the π bond of benzene, donates a pair of electrons forming a 6-bond. A species with a + ve charge is formed as an intermediate. This is called ‘arenium ion’ and is stabilised by Resonance.
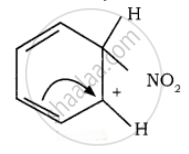
In the last step, the hydrogen atom attached to the carbon carrying the nitro group is pulled out as a proton, by the Lewis base HSO4–, so that stable aromatic system is formed.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Predict the possible product of the following reaction.
bromination of phenol
Name two reagents used for acylation of benzene.
Major product of the below mentioned reaction is, \[\ce{(CH3 )2 C = CH2 ->[ICI]}\]
Some meta-directing substituents in aromatic substitution are given. Which one is most deactivating?
How will you convert ethyl chloride into ethane?
Write the structure of the following alkanes.
2, 3 – Dimethyl – 6 – (2 – methyl propyl) decane
Identify the hydrocarbon compound from following containing carbon atoms in the range of C6 to C8?
A compound with molecular formula C4H4O has all the four carbon atom and the oxygen atom in the ring. It also has two carbon-carbon double bonds. The compound is ____________.
Which of the following is INCORRECT for aromatic hydrocarbons?
Read the following reaction and answer the questions given below.
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{..............................}\ce{CH3}\\
\phantom{...........................}|\\
\ce{CH3 - C = CH2 + HBr->[Benzoyl][peroxide] H3C - CH - CH2Br}\\
|\phantom{....................................}\\
\ce{CH3}\phantom{.................................}
\end{array}\]
- Write the IUPAC name of the product.
- State the rule that governs the formation of this product.
