Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
How does Huckel rule help to decide the aromatic character of a compound?
Solution
In 1865, August Kekule suggested that benzene consists of a cyclic planar structure of six carbon with alternate single and double bonds.
There were two objections:
- Benzene forms only one ortho disubstituted products whereas the Kekule’s structure predicts two o-di substituted products as shown below.

- Kekule’s structure failed to explain why benzene with three double bonds did not give addition reactions like other alkenes.To overcome this objection, Kekule suggested that benzene was mixture of two forms (1 and 2) which are in rapid equilibrium.

- Resonance description of benzene:
The phenomenon in which two or more structures can be written for a substance which has an identical position of atoms is called resonance. The actual structure of the molecule is said to be resonance hybrid of various possible alternative structures. In benzene, Kekule’s structures I & II represented the resonance structure, and structure III is the resonance hybrid of structure I & II.
The structures 1 and 2 exist only in theory. The actual structure of benzene is the hybrid of two hypothetical resonance structures.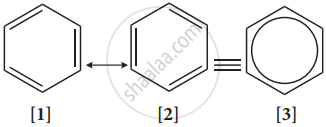
- Spectroscopic measurements:
Spectroscopic measurements show that benzene is planar and all of its carbon-carbon bonds are of equal length 1.40 Å. This value lies between carbon-carbon single bond length 1.54 Å and carbon-carbon double bond length 1.34 Å. - Molecular orbital structure:
The structure of benzene is best de¬scribed in terms of the molecular orbital theory. All the six carbon atoms of benzene are sp2 hybridized. Six sp2 hybrid orbitals of carbon linearly overlap with six 1 s orbitals of hydrogen atoms to form six C – H sigma bonds. Overlap between the remaining sp2 hybrid orbitals of carbon forms six C – C sigma bonds.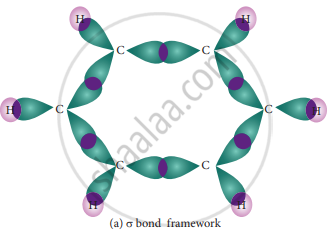
- Formation of Sigma bond in benzene-
All the σ bonds in benzene lie in one plane with a bond angle of 120°. Each carbon atom in benzene possess a un hybridized p-orbital containing one electron. The lateral overlap of their p-orbital produces 3 π- bond. The six electrons of the p-orbitals cover all the six carbon atoms and are said to be delocalized. Due to delocalization, strong π-bond is formed which makes the molecule stable. Hence unlike alkenes and alkynes benzene undergoes substitution reactions rather addition reactions under normal conditions.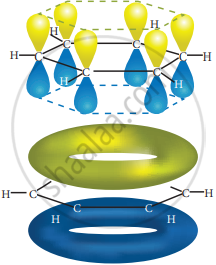
All carbon atoms have the delocalized π MO is formed by p-orbitais the overlap of six p-orbitals. - Representation of benzene:
Hence, there are three ways in which benzene can be represented.
Expanded form-
Kekule structure-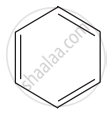
Short hand representation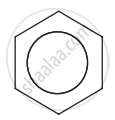
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
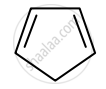
Identify giving reason whether the following compound is aromatic or not.
Identify the compound (A) in the following reaction
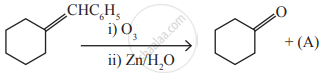
Some meta-directing substituents in aromatic substitution are given. Which one is most deactivating?
Describe the mechanism of Nitration of benzene.
Suggest the route for the preparation of the following from benzene.
m - dinitro benzene
Write the structure of the following alkanes.
5 – (2 – Ethyl butyl) – 3, 3 – dimethyldecane
How will you prepare propane from a sodium salt of fatty acid?
Which among the following compounds has highest boiling point?
Which of the following compounds on bromination yields ![]() ?
?
Conversion of hexane into benzene involves the reaction of ______.
