Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Diagrams (a) and (b) in figure below show the refraction of a ray of light of single colour through a prism and a parallel sided glass slab respectively.
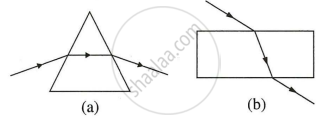
- In each diagram, label the incident, refracted, emergent rays and the angle of deviation.
- In what way the direction of emergent ray in the two cases differ with respect to the incident ray? Explain your answer.
Solution
-
-
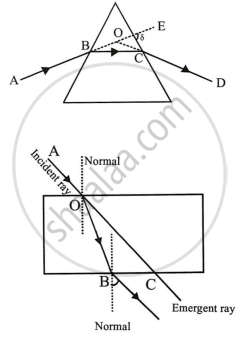
AB stands for the incident ray. BC stands for a refracted ray. CD stands for emergent radiation. The angle of deviation is ∠EOD, where the incident ray produced forward meets the emerging ray produced backward.
-
AO stands for incident radiation. OB stands for a refracted ray. BC stands for the emerging ray. There is no angle of deviation, since the incident ray in a glass block is parallel to the emergent ray.
-
-
In the glass prism, the incident beam AB would have gone along ABEF in the absence of the prism. It seems that the emergent ray CD is progressing ECD. Thus, the ray AB has been deviated through ∠FED = δ along CD.
In the slab of glass, emergent ray CD emerges in a rare medium, deviates from the normal, and is parallel to incident ray AB.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Which of the two prism, A made of crown glass and B made of flint glass, deviates a ray of light more?
How does the angle of deviation depend on the refracting angle of the prism?
A ray of light is normally incident on one face of an equilateral glass prism. Answer the following:
What is the angle of incidence on the first face of the prism?
A ray of light suffers refraction through an equilateral prism. The deviation produced by the prism does not depend on the ______.
What should be the angle of incidence for a ray of light which suffers a minimum deviation of 36° through an equilateral prism?
[Hint: A = 60°, i = (A + δmin)/2]
In an experiment to trace the path of a ray of light through a glass prism for different values of angle of incidence a student would find that the emergent ray:
A prism ABC (with BC as base) is placed in different orientations. A narrow beam of white light is incident on the prism as shown in below Figure. In which of the following diagrams, after dispersion, the third colour from the top of the spectrum corresponds to the colour of the sky?
Explain the phenomenon of dispersion of white light through a glass prism, using suitable ray diagram.
Name the colour of white light which is deviated the least on passing through a prism.