Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Discuss the law of transverse vibrations in stretched strings.
Solution
There are three laws of transverse vibrations of stretched strings that are given as follows:
- The law of length:
For a given wire with tension T (which is fixed) and mass per unit length µ (fixed) the frequency varies inversely with the vibrating length. Therefore,
`"f" prop 1/l = "f" = "C"/l`
⇒ l × f = C, where C is a constant
- The law of tension:
For a given vibrating length l (fixed) and mass per unit length p, (fixed) the frequency varies directly with the square root of the tension T,
f = `prop sqrt"T"`
`=> "f" = "A"sqrt"T"`, where A is a constant - The law of mass:
For a given vibrating length l (fixed) and tension T (fixed) the frequency varies inversely with the square root of the mass per unit length µ,
`"f" prop 1/sqrtmu`
`=> "f" = "B"/sqrtmu`, where B is a constant
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
For a particular tube, among six harmonic frequencies below 1000 Hz, only four harmonic frequencies are given: 300 Hz, 600 Hz, 750 Hz and 900 Hz. What are the two other frequencies missing from this list?
Let y = `1/(1 + x^2)` at t = 0 be the amplitude of the wave propagating in the positive x-direction. At t = 2s, the amplitude of the wave propagating becomes y = `1/(1 + (x - 2)^2)`. Assume that the shape of the wave does not
change during propagation. The velocity of the wave is:
What is a stationary wave?
Explain the formation of stationary waves.
Write the characteristics of stationary waves.
Explain the concepts of fundamental frequency, harmonics and overtones in detail.
What is a sonometer? Give its construction and working. Explain how to determine the frequency of tuning fork using a sonometer.
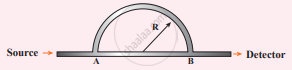
A sound wave is transmitted into a tube as shown in the figure. The sound wave splits into two waves at point A which recombine at point B. Let R be the radius of the semi-circle which is varied until the first minimum. Calculate the radius of the semi-circle if the wavelength of the sound is 50.0 m.
Police in a siren car moving with a velocity 20 ms– chases a thief who is moving in a car with a velocity v0 ms-1. The police car sounds at frequency 300 Hz, and both of them move towards a stationary siren of frequency 400 Hz. Calculate the speed in which thief is moving. (Assume the thief does not observe any beat)
