Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Explain the concepts of fundamental frequency, harmonics and overtones in detail.
Solution
Fundamental frequency and overtones: Let us now keep the rigid boundaries at x = 0 and x = L and produce standing waves by wiggling the string (as in plucking strings in a guitar). Standing waves with a specific wavelength are produced. Since, the amplitude must vanish at the boundaries, therefore, the displacement at the boundary must satisfy the following conditions
x(x = 0, t) = 0 and y(x = L, t) = 0
Since, the nodes formed at a distance `(lambda_"n")/2` apart, we have `"n"(lambda_"n"/2)` = L,
where n is an integer, L is the length between the two boundaries and λn is the specific wavelength that satisfy the specified boundary conditions. Hence,
`lambda_"n" = ((2"L")/"n")` ...(2)
Therefore, not all wavelengths are allowed. The (allowed) wavelengths should fit with the specified boundary conditions, i.e., for n = 1, the first mode of vibration has a specific wavelength λ1 = 2L. Similarly for n = 2, the second mode of vibration has a specific wavelength
`lambda_2 = ((2"L")/2)` = L
For n = 3, the third mode of vibration has specific wavelength
`lambda_3 = ((2"L")/3)` and so on.
The frequency of each mode of vibration (called natural frequency) can be calculated.
We have, `"f"_"n" = "v"/lambda_"n" = "n"("v"/"2L")` ...(3)
The lowest natural frequency is called the fundamental frequency.
`"f"_1 = "v"/lambda_1 = ("v"/"2L")` ....(4)
The second natural frequency is called the first over tone.
`"f"_2 = 2("v"/"2L") = 1/"L" sqrt("T"/mu)`
The third natural frequency is called the second over tone.
`"f"_3 = 3("v"/"2L") = 3 (1/"2L" sqrt("T"/mu))` and so on.
Therefore, the nth natural frequency can be computed as integral (or integer ) multiple of the fundamental frequency, i.e.,
fn = nf1 where n is an integer …(5)
If natural frequencies are written as an integral multiple of fundamental frequencies, then the frequencies are called harmonics. Thus, the first harmonic is f1 = f1 (the fundamental frequency is called first harmonic), the second harmonic is f2 = 2f1, the third harmonic is f3 = 3f1 etc.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
For a particular tube, among six harmonic frequencies below 1000 Hz, only four harmonic frequencies are given: 300 Hz, 600 Hz, 750 Hz and 900 Hz. What are the two other frequencies missing from this list?
Let y = `1/(1 + x^2)` at t = 0 be the amplitude of the wave propagating in the positive x-direction. At t = 2s, the amplitude of the wave propagating becomes y = `1/(1 + (x - 2)^2)`. Assume that the shape of the wave does not
change during propagation. The velocity of the wave is:
What is a stationary wave?
Explain the formation of stationary waves.
Write the characteristics of stationary waves.
Discuss the law of transverse vibrations in stretched strings.
What is a sonometer? Give its construction and working. Explain how to determine the frequency of tuning fork using a sonometer.
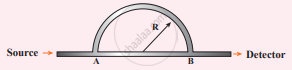
A sound wave is transmitted into a tube as shown in the figure. The sound wave splits into two waves at point A which recombine at point B. Let R be the radius of the semi-circle which is varied until the first minimum. Calculate the radius of the semi-circle if the wavelength of the sound is 50.0 m.
Police in a siren car moving with a velocity 20 ms– chases a thief who is moving in a car with a velocity v0 ms-1. The police car sounds at frequency 300 Hz, and both of them move towards a stationary siren of frequency 400 Hz. Calculate the speed in which thief is moving. (Assume the thief does not observe any beat)
