Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Does public debt impose a burden? Explain.
Solution
Government debt or public debt refers to the amount or money that a central government owes. This amount may be borrowings of the government from banks, public financial institutions and from other external and internal sources. Public debt definitely imposes a burden on the economy as a whole, which is described through the following points.
1. Adverse effect on productivity and investment :-
A government may impose taxes or get money printed to repay the debt. This however reduces the peoples’ ability to work, save and invest, thus hampering the development of a country.
2. Burden on younger generations :-
The government transfers the burden of reduced consumption on future generations. Higher government borrowings in the present leads to higher taxes levied in future in order to repay the past obligations. The government imposes taxes on the younger generations, lowering their consumption, savings and investments. Hence, higher public debt has negative effect on the welfare of the younger generations.
3. Lowers the private investment :-
The government attracts more investment by raising rates of interests on bonds and securities. As a result, a major part of savings of citizens goes in the hands of the government, thus crowding out private investments.
4. Leads to the drain of National wealth :-
The wealth of the country is drained out at the time of repaying loans taken from foreign countries and institutions.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Define fiscal deficit
Define revenue
Consider an economy described by the following functions:- C = 20 + 0.80Y, I = 30, G = 50, TR = 100 (a) Find the equilibrium level of income and the autonomous expenditure multiplier in the model. (b) If government expenditure increases by 30, what is the impact on equilibrium income? (c) If a lump-sum tax of 30 is added to pay for the increase in government purchases, how will equilibrium income change?
We suppose that C = 70 + 0.70Y D, I = 90, G = 100, T = 0.10Y (a) Find the equilibrium income. (b) What are tax revenues at equilibrium Income? Does the government have a balanced budget?
Are fiscal deficits inflationary?
What do you understand by G.S.T?
Classify the following statement into positive economic or normative economic, with suitable reason:
Government should try to control the rising fiscal deficit.
Suppose you are a member of the "Advisory Committee to the Finance Minister of India". The Finance Minister is concerned about the rising Revenue Deficit in the budget.
Suggest anyone measure to control the rising Revenue Deficit of the government.
The primary deficit in a government budget is ______.
Which of the following statement is true?
| S. No. | Content | Rs (in crores) |
| 1. | Revenue Expenditure | 100 |
| 2. | Capital Receipts | 40 |
| 3. | Net Borrowings | 38 |
| 4. | Net Interest Payments | 27 |
| 5. | Tax Revenue | 50 |
| 6. | Non-tax Revenue | 15 |
Which of the following is MOST LIKELY to be the main contributor to the fiscal deficit in this case?
Which of the following factors necessitated the need for economic reforms?
The difference between fiscal deficit and interest payment is known as ______
How do we get the primary deficit from the fiscal deficit?
Identify the correctly matched pair of the items in Column A to those in Column B:
| Column A | Column B | ||
| 1 | Fiscal Deficit | (a) | Other than interest payments |
| 2 | Primary Deficit | (b) | Borrowings less interest payments |
| 3 | Revenue Deficit | (c) | Borrowings |
| 4 | Tax Deficit | (d) | Borrowings in government budget |
Primary deficit is borrowing requirements of government for making:
Fiscal Deficit equals:
The shape of average revenue curve in monopoly is ______
Compare the trends depicted in the figures given below:
| Figure 1: Trends in Fiscal deficit and Primary deficit |
Figure 2: Fiscal deficit as a percent of Budget estimate |
 |
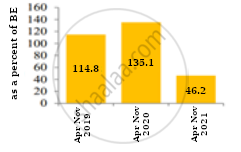 |
