Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Does public debt impose a burden? Explain.
उत्तर
Government debt or public debt refers to the amount or money that a central government owes. This amount may be borrowings of the government from banks, public financial institutions and from other external and internal sources. Public debt definitely imposes a burden on the economy as a whole, which is described through the following points.
1. Adverse effect on productivity and investment :-
A government may impose taxes or get money printed to repay the debt. This however reduces the peoples’ ability to work, save and invest, thus hampering the development of a country.
2. Burden on younger generations :-
The government transfers the burden of reduced consumption on future generations. Higher government borrowings in the present leads to higher taxes levied in future in order to repay the past obligations. The government imposes taxes on the younger generations, lowering their consumption, savings and investments. Hence, higher public debt has negative effect on the welfare of the younger generations.
3. Lowers the private investment :-
The government attracts more investment by raising rates of interests on bonds and securities. As a result, a major part of savings of citizens goes in the hands of the government, thus crowding out private investments.
4. Leads to the drain of National wealth :-
The wealth of the country is drained out at the time of repaying loans taken from foreign countries and institutions.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Define revenue
‘The fiscal deficit gives the borrowing requirement of the government’. Elucidate.
Suppose that for a particular economy, investment is equal to 200, government purchases are 150, net taxes (that is lump-sum taxes minus transfers) is 100 and consumption is given by C = 100 + 0.75Y (a) What is the level of equilibrium income? (b) Calculate the value of the government expenditure multiplier and the tax multiplier. (c) If government expenditure increases by 200, find the change in equilibrium income.
Consider an economy described by the following functions:- C = 20 + 0.80Y, I = 30, G = 50, TR = 100, calculate the effect on output of a 10 per cent increase in transfers, and a 10 per cent increase in lump-sum taxes. Compare the effects of the two.
Answer the following question.
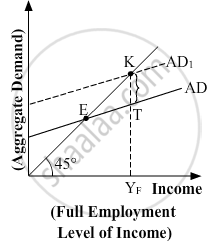
In the given figure, what does the gap 'KT' represent? State any two fiscal measures to correct the situation.
Regressive tax is that which is ______.
The primary deficit in a government budget is ______.
When the revenue receipts are less than the revenue expenditures in a government budget, this shortfall is termed as
What is relation between government deficit and government debt?
______ are those transactions that are undertaken to cover deficit or surplus in autonomous transactions.
Which of the following transactions are correct about ORT?
How do we get the primary deficit from the fiscal deficit?
If India exports goods worth ₹20 crores and imports goods worth ₹30 crores, it will have a ______
Which of the following points are related to the current alarm?
Identify the correctly matched pair of the items in Column A to those in Column B:
| Column A | Column B | ||
| 1 | Fiscal Deficit | (a) | Other than interest payments |
| 2 | Primary Deficit | (b) | Borrowings less interest payments |
| 3 | Revenue Deficit | (c) | Borrowings |
| 4 | Tax Deficit | (d) | Borrowings in government budget |
Identify which of the following statements is true.
On the basis of the given information, calculate the value of:
- Fiscal deficit
- Primary deficit
| S.No. | Items | 2021-22 (₹ in crore) |
| (i) | Revenue Receipts | 20 |
| (ii) | Capital Expenditure | 15 |
| (iii) | Revenue Deficit | 10 |
| (iv) | Non-debt creating capital receipts | 50% of revenue receipts |
| (v) | Interest Payments | 4 |
