Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
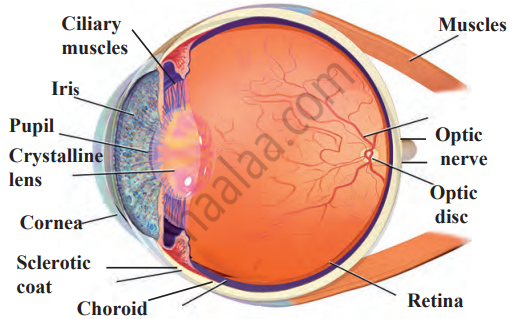
Draw a neat and labelled diagram of the structure of the human eye.
Solution
RELATED QUESTIONS
Write the function of the following part of the human eye: Cornea
Write the function of the following part of the human eye: ciliary muscles
The human eye can focus objects at different distances by adjusting the focal length of the eye lens. This is due to ______.
Describe the anatomy of the human eye.
Name two parts of the eye which refract light rays (or bend light rays).
What is the name of:
the light-sensitive layer in the eye?
Name that part of the eye which is equivalent to the photographic film in a camera.
Out of rods and cones m the retina of your eye:
which detect colour?
What changes the shape of lens in the eye?
What is the least distance of distinct vision for a normal human eye?
There are two types of light-sensitive cells in the human eye:
Where are they found?
What happens to the size of pupil of our eye (i) in dim light (ii) in bright light?
Why does the eye-lens not have to do all the work of converging incoming light rays?
What are the advantages of having two eyes instead of just one?
Name two animals having eyes:
one the sides of the head.
Name the following:
The part of the eye responsible for its shape.
Mention if the following statement is true (T) or false (F) Give reason.
yellow spot of the retina is the region of colour vision
Given below is certain structure. Write against them its functional acivity.
retina and ……………………….
The figure below compares a part of our eye with a part of a photographic camera.

Name the corresponding parts of the eye the camera shown here that are comparable in function.
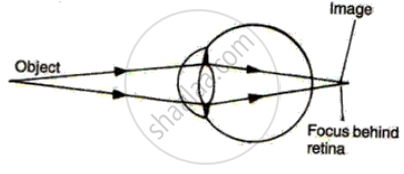
The diagram alongside represents a certain defect of vision of the human eye.
(i) Name the defect.
(ii) Describe briefly the condition in the eye responsible for the defect.
(iii) Redraw the figure by adding a suitable lens correcting the defect. Label the parts through which light-rays pass.
(iv) What special advantage do human beings derive in having both eyes facing forward?
Differentiate between:
Yellow spot and Blind spot.
Name the following:
The type of lens used for correcting myopia.
Give Technical Term:
The cells of the retina that are sensitive to colour.
Give Technical Term:
Name the part of the retina on which an object is focused for the clearest vision.
Give Technical Term:
The adjustment of the eye in order to obtain a clear vision of objects at different distances
State the Function:
Iris
State the Function:
Cornea
A small hole of changing diameter at the centre of Iris is called _______.
The image of an object at an infinite distance is obtained in a real and erect form through a convex magnifying glass.
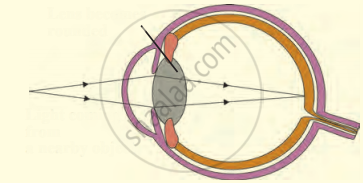
The following figure show the change in the shape of the lens while seeing distant and nearby objects. Complete the figures by correctly labelling the diagram.
The larynx has fold of tissue which vibrate with the passage of air to produce sound.
Shylesh is a school-going kid studying standard VIII. He is crazy about playing video games on mobile phones. After a couple of months, his eyes turned red and he felt severe pain in his eyes. His science teacher enquired about this and advised his parents to take him to an eye doctor.
- How does excessive usage of mobile phone affect our eyes?
- What are the values shown by the teacher?
With reference to human eye, answer the following question.
What is aqueous humor?
Match the following:
| Column - I | Column - II |
| 1. Retina | a. Pathway of light |
| 2. Pupil | b. Far point comes closer |
| 3. Ciliary muscles | c. near point moves away |
| 4. Myopia | d. Screen of the eye |
| 5. Hypermetropia | f. Power of accommodation |
Match the following:
| Column - I | Column - II | ||
| 1 | Retina | a | pathway of light |
| 2 | Pupil | b |
far point comes closer |
| 3 | Ciliary muscles | c |
near point moves away |
| 4 | Myopia | d | screen of the eye |
| 5 | Hypermetropia | e | power of accommodation |
| Column I | Column II | ||
| 1 | Retina | a | Path way of light |
| 2 | Pupil | b | Far point comes closer |
| 3 | Ciliary muscles | c | near point moves away |
| 4 | Myopia | d | Screen of the eye |
| 5 | Hypermetropia | e | Power of accomodation |
Name the following:
Place of no vision in the retina of the eye.
Which of the following is responsible for the adjustment of the size of pupil?
