Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Draw a sketch of equipotential surfaces due to a single charge (-q), depicting the electric field lines due to the charge
Solution
Equipotential surface for a negative charge:

APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Two charges 2 μC and −2 µC are placed at points A and B 6 cm apart.
- Identify an equipotential surface of the system.
- What is the direction of the electric field at every point on this surface?
Draw the equipotential surfaces due to an electric dipole. Locate the points where the potential due to the dipole is zero.
Depict the equipotential surfaces for a system of two identical positive point charges placed a distance(d) apart?
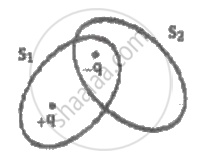
S1 and S2 are the two imaginary surfaces enclosing the charges +q and -q as shown. The electric flux through S1 and S2 are respectively ______.
The diagrams below show regions of equipotentials.
(i) |
(ii)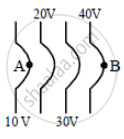 |
(iii) |
(iv) |
A positive charge is moved from A to B in each diagram.
- The potential at all the points on an equipotential surface is same.
- Equipotential surfaces never intersect each other.
- Work done in moving a charge from one point to other on an equipotential surface is zero.
The work done to move a charge along an equipotential from A to B ______.
- cannot be defined as `- int_A^B E.dl`
- must be defined as `- int_A^B E.dl`
- is zero.
- can have a non-zero value.
Prove that a closed equipotential surface with no charge within itself must enclose an equipotential volume.
Draw equipotential surfaces for (i) an electric dipole and (ii) two identical positive charges placed near each other.
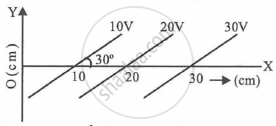
Equipotential surfaces are shown in figure. Then the electric field strength will be ______.