Advertisements
Advertisements
Questions
Explain any three types of price elasticity of demand with the help of diagrams.
Discuss five cases of elasticity of demand.
Explain the different types of price elasticity of demand with the help of diagrams.
Solution
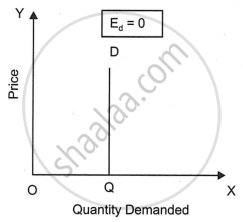
- Perfectly Inelastic Demand: When quantity demanded does not change at all as a result of change in price of the commodity, demand of that commodity is said to be perfectly inelastic. In such a case, quantity demanded is independent of price changes. Demand here is non-responsive and the numerical value of price elasticity (Ed) will be zero. Demand curve will be parallel to Y-axis as shown in Figure. In the figure, demand (OQ) is fixed. If price increases or decreases, it remains unchanged. This type of situation is normally not found in our real life.
- Unit Elastic Demand: In this situation, percentage change in demand is equal to percentage change in price. For instance, if price of milk rises by 20 per cent and consequently its demand also falls by 20 per cent, price elasticity of demand will be unitary elastic. According to Dr. Marshall, if elasticity of demand is equal to unity, total expenditure of the commodity remains the same even when the price changes. Cases of unitary elasticity are very rare.
Elasticity of demand will be unity when the demand curve takes the shape of rectangular hyperbola. Rectangular hyperbola is a curve under which all rectangular areas are equal. Each rectangular area shows the total expenditure (price x quantity) spent on the commodity at various prices.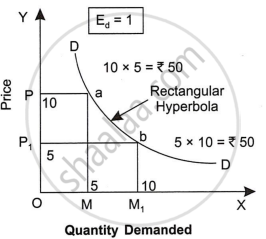
- Perfectly Elastic Demand Curve: It is a situation in which a small change in price causes an infinitely large change in quantity demanded. A small rise in price on the part of the seller reduces the demand to zero. A small reduction in price, will increase the demand to infinity (i.e., no seller is able to satisfy this demand at the reduced price). In our real life, we do not have any such commodity which has perfectly elastic demand. Here, elasticity of demand is equal to infinity and demand curve becomes parallel to X-axis as shown in Figure. Alternatively speaking, here quantity demanded is independent of price. Price is given.
Demand for a good can be perfectly elastic only when there are some perfect substitutes of the good are available in the market. But perfect substitutes are not found in real life.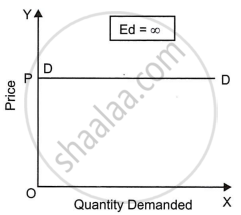
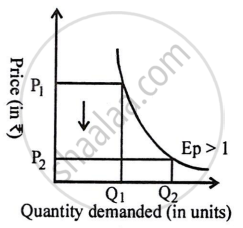
- Highly Elastic Demand: Highly elastic demand occurs when a proportionate change in price results in a greater than proportionate change in demand.
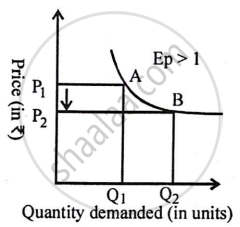
- Highly inelastic demand: Demand is very inelastic when a proportional change in price results in a less-than-proportional change in demand.
Notes
Students should refer to the answer according to their questions.
RELATED QUESTIONS
Give economic term:
Degree of responsiveness of quantity demanded to change in income only.
Degree of responsiveness of a change in quantity demanded to a change in the income of the consumer −
Find the odd word
Types of elasticity of demand -
Assertion (A): A change in quantity demanded of one commodity due to a change in the price of other commodity is cross elasticity.
Reasoning (R): Changes in consumers income leads to a change in the quantity demanded.
With the help of a diagram, explain the Relatively inelastic demand curve.
Define income elasticity of demand.
Assertion (A): A change in quantity demanded of one commodity due to a change in the price of other commodity is cross elasticity.
Reasoning (R): Changes in consumers' income lead to a change in the quantity demanded.
Assertion (A): A change in quantity demanded of one commodity due to a change in the price of other commodity is cross elasticity.
Reasoning (R): Changes in consumers income leads to a change in the quantity demanded.
Define the term price elasticity of demand.
If prices of salt and coffee increase by the same proportion, will their quantity demanded behave in the same manner? Explain by giving reasons.
With the help of a diagram, explain the Unitary elastic demand curve.
Why is price elasticity of demand negative?
What will be the effect of 10 percent rise in price of a good on its demand if price elasticity of demand is zero?
What will be the effect of 10 percent rise in price of a good on its demand if price elasticity of demand is −1?
What will be the effect of 10 percent rise in price of a good on its demand if price elasticity of demand is −2?
Price elasticity of demand shows:
Given values of price elasticities of demand, less 'elastic' demand is ______.
