Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
1: Elementary Theory of Demand
▶ 2: Elasticity of Demand
3: Theory of Supply
Unit II - Factors of Production : Basic Concepts
4: Factors of Production
Unit III - Alternative Market Structures : Basic Concepts
5: Nature and Structure of Markets
Unit IV - The State and Economic Development
6: The State and Economic Development
Unit V - Money and Banking : Basic Concepts
7: Meaning and Functions of Money
8: Commercial Banks
9: Central Banks
10: Inflation
![Goyal Brothers Prakashan solutions for Economic Application [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 2 - Elasticity of Demand Goyal Brothers Prakashan solutions for Economic Application [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 2 - Elasticity of Demand - Shaalaa.com](/images/economic-application-english-class-10-icse_6:4ae302fabf354f56a3e776b0889e746c.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 2: Elasticity of Demand
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 2 of CISCE Goyal Brothers Prakashan for Economic Application [English] Class 10 ICSE.
Goyal Brothers Prakashan solutions for Economic Application [English] Class 10 ICSE 2 Elasticity of Demand QUESTIONS [Pages 40 - 44]
Multiple Choice Questions
Degrees of price elasticity of demand is of ______ types.
three
five
two
four
Which is the implication of a horizontal demand curve?
Perfectly elastic demand
Perfectly inelastic demand
Inelastic demand
Elastic demand
Which of the following goods have inelastic demand?
Textbooks
Air conditioners
Cars
Precious clothes
The coefficient of price elasticity of a good is 0.8, its demand will said to be ______.
elastic
inelastic
perfectly elastic
perfectly inelastic
A demand curve which takes the form of a vertical line parallel to the price axis illustrates elasticity which is ______.
Zero
Infinite
> 1
1
The demand curve is horizontal
What will be the value of price elasticity in this case?
Ed = 0
Ed > 1
Ed = ∞
Ed = 0
The demand curve is vertical
What will be the value of price elasticity in this case?
Ed = 1
Ed = 0
Ed = 0
Ed = ∞
Price elasticity of demand is defined as the percentage change in the quantity demanded of a commodity divided by the percentage change in the price of that commodity.
True
False
If elasticity of demand for salt is zero, and household demands 2 kg. of salt during one month when its price is ₹ 5 per kg., this household will demand the same quantity of salt even if price rises to ₹ 8 per kg.
True
False
As a result of 5% fall in the price of a good, its demand rises by 12%, the demand for the good will said be ______.
relatively less elastic demand
relatively more elastic demand
Perfectly inelastic demand
Perfectly elastic demand
Match the following and select the correct option.
| Column I | Column II | ||
| (i) | Perfectly elastic demand | A. | Ed = 0 |
| (ii) | Perfectly inelastic demand | B. | Ed = ∞ |
| (iii) | Relatively elastic demand | C. | Ed < 1 |
| (iv) | Relatively inelastic demand | D. | Ed > 1 |
(i) A, (ii) D, (iii) C, (iv) B
(i) A, (ii) B, (iii) D, (iv) C
(i) B, (ii) A, (iii) D, (iv) C
(i) D, (ii) C, (iii) A, (iv) B
When change in price is greater than the change in quantity demand it is a case of elastic demand.
True
False
- Luxuries goods have generally elastic demand.
- Goods whose close substitutes are available have inelastic demand.
Statement (i) is false and statement (ii) is true
Statement (i) is true and statement (ii) is false
Both (i) and (ii) are false
Both (i) and (ii) are true
Elasticity of demand for two goods A and B is -2 and -3 respectively. Then good A has higher elasticity.
True
False
The government wants to reduce the consumption of good by 10%. The price elasticity of demand for elasticity is -0.4. The government should raise the price of elasticity by ______.
2%
25%
0.4%
4%
What is the implication of a vertical demand curve?
Perfectly inelastic demand
Perfectly elastic demand
Relatively inelastic demand
Unitary elastic demand
As a result of a 5% increase in price, the demand for commodity X increases by 12%. The price elasticity of demand will be ______.
eD > 1
eD < 1
eD = 1
eD = ∞
The price of a commodity goes up from ₹ 26 to ₹ 30 as a result of which demand falls from 4 units to 2 units, the price elasticity of demand is ______.
2.25
3.25
3.50
3.75
The price of Y falls from ₹ 8 to ₹ 6. The quantity demanded increases from 100 units to 125 units. The price electricity of demand will be ______.
.0625
0.625
1
6.25
Price elasticity of demand measures ______.
Change in price caused by cnange in demand.
The rate of change of demand.
The responsiveness of demand to a change in price.
The responsiveness of demand to a change in income.
If the price of a commodity decreases from ₹ 70 per unit to ₹ 60 per unit and the quantity demanded remains the same, then the price elasticity of demand for that commodity will be ______.
Infinity
Zero
One
Less than one
When the price elasticity of demand for a good equals ______.
0, the demand cure is horizontal
1, the demand curve is vertical
1, the demand curve is horizontal
0, the demand curve is vertical
If the percentage increase in the quantity of a commodity is smaller than the percentage fall in its price, the coefficient of price elasticity of demand is ______.
greater than 1
equal to 1
smaller than 1
zero
Which of the following is the most likely reason for the relatively high elasticity of bottled water?
Many substitutes are available
Good for health
Can be used for many purposes
Necessity item
Assertion-Reasoning & Matching Based Questions
Assertion (A): The demand for soap, salt, matches etc. is highly elastic.
Reason (R): The demand for soap, salt, matches etc. is highly inelastic because the consumer spends a very small amount of expenditure in relation to his/her income.
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Assertion (A) is true but Reason (R) is false.
Assertion (A) is false but Reason (R) is true.
Assertion (A): Suppose that a 2 per cent drop in the price of chocolate causes a 2 per cent increase in quantity demanded. This case is termed unit elasticity.
Reason (R): In this example, Ed is exactly 1 (or unity). Ed = `2/2=1`
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Assertion (A) is true but Reason (R) is false.
Assertion (A) is false but Reason (R) is true.
Match the following:
| Column I | Column II |
| A. Perfectly Elastic | (i) Ed = 0 |
| B. Perfectly Inelastic | (ii) Ed = infinity |
| C. Highly Elastic | (iii) Ed < I |
| D. Less Elastic | (iv) Ed > I |
A. (ii), B. (iii), C. (iv) D. (iii)
A. (ii), B. (i) c. (iv), D. (iii)
A (ii), B. (iii), c. (iii) D. (iii)
A. (iii), B. (ii), C. (iv), D. (i)
Match the following:
| Column I | Column II |
| A. Goods whose close substitutes are available | (i) Perfectly elastic demand |
| B. Goods whose demand cannot be postponed | (ii) Perfectly inelastic demand |
| C. Goods whose quantity demanded does not respond to price change | (iii) Elastic demand |
| D. Goods which are perfect substitutes | (iv) Inelastic demand |
A. (ii) B. (iii) C. (iv) D. (i)
A. (ii) B. (i) C. (iv) D. (iii)
A (ii) B. (iii) C. (iv) D. (i)
A. (iii) B. (iv) C. (ii) D. (i)
Assertion (A): Demand for a commodity with large number of substitutes with be less elastic.
Reason (R): With large number of substitutes, even a small rise in its price will induce the buyers to go for its substitutes.
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A) .
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Assertion (A) is true but Reason (R) is false.
Assertion (A) is false but Reason (R) is true.
Short Answer Type Questions
Define the term price elasticity of demand.
When is the demand for a commodity is said to be elastic?
When is the demand for a commodity said to be perfectly inelastic?
If commodity X and Y are complementary goods , what will be the cross elasticity of demand?
Would the elasticity of demand in the following case be unity, less than unity or greater than unity?
A rise in the price of a commodity reduces the total expenditure.
Would the elasticity of demand in the following case be unity, less than unity or greater than unity?
A rise in the price of a commodity increases total expenditure.
Would the elasticity of demand in the following case be unity, less than unity or greater than unity?
A fall in the price of a commodity increases total expenditure.
Would the elasticity of demand in the following case be unity, less than unity or greater than unity?
A fall in the price of commodity, the total expenditure remains the same.
Draw a diagram showing a perfectly elastic demand curve.
Draw a diagram showing the Elasticity of demand less than one.
Select the commodities from the following which have inelastic demand:
Car
Textbooks
Cigarettes
Diamonds
Milk
Coal
Coke
Is the demand for the following commodities elastic or inelastic?
- Salt
- Foodgrains
- Petrol
- Needles
- Green vegetables
- Four Square cigarettes
- Water
For each of the following, state whether it has inelastic demand or elastic demand:
- Luxury cars
- Life saving drugs
- Salt
- English textbook of class X
When the price of a commodity falls by 80%, the quantity demanded increases by 100%. Find out its price elasticity of demand.
Ed = `100/80 = 1.25`
Explain any two factors that affect the price elasticity of demand. Give suitable examples.
The nature of a commodity determines its price elasticity of demand. Explain.
State the formula for calculating the price elasticity of demand using the percentage method.
The price of a commodity falls from ₹15 to ₹10. As a result, demand rises from 100 units to 150 units, Use the expenditure method to find the price elasticity of demand.
Study the table given below and state whether demand is elastic or inelastic. Give reasons for your answer.
| Price in (₹) | Total outlay (₹) |
| 5 | 25 |
| 3 | 18 |
How does the availability of substitutes of a commodity affect its price elasticity of demand?
Indicate the degree of elasticity of demand of the following demand curves.
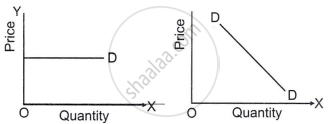
The price of milk rises from ₹ 26.00 to ₹ 30.00 per litre and its demand falls from four litres per day to two litres per day. Calculate the elasticity demand for milk.
A consumer purchased 10 units of a commodity when its price was ₹ 5 per unit. He purchases 12 units of the commodity when price falls to ₹ 4 per unit. Calculate the price elasticity of demand for the commodity.
When % change in demand is greater than % change in price, it is a case of inelastic demand. Write true or false. Give reason.
True
False
Long Answer Type Questions
Explain any three types of price elasticity of demand with the help of diagrams.
Define elasticity of demand.
Explain briefly the factors on which elasticity of demand depends.
Define the term price elasticity of demand.
How do we determine whether the demand for a particular commodity is elastic or inelastic?
State the formula for calculating the price elasticity of demand using the percentage method.
If prices of salt and coffee increase by the same proportion, will their quantity demanded behave in the same manner? Explain by giving reasons.
Define the term price elasticity of demand.
Define the term price elasticity of demand.
With the help of a diagram, explain the condition when EP > 1.
With the help of a diagram, explain the condition when EP < 1.
With the help of a diagram, explain the condition when Ep = 1.
Define the term price elasticity of demand.
With the help of a diagram, explain the Relatively inelastic demand curve.
With the help of a diagram, explain the Relatively elastic demand curve.
With the help of a diagram, explain the Unitary elastic demand curve.
Goyal Brothers Prakashan solutions for Economic Application [English] Class 10 ICSE 2 Elasticity of Demand QUESTION BANK [Pages 44 - 48]
Define the term price elasticity of demand.
Why is price elasticity of demand negative?
When is the demand for a commodity is said to be elastic?
When is the demand of a commodity said to be inelastic?
Give two examples of inelastic demand.
What is meant by unitary elastic demand?
Give two examples of unitary elastic demand.
When is the demand for a commodity said to be perfectly inelastic?
When will the demand curve be parallel to x-axis?
Comment upon the shape of the demand curve, if Ed = 0.
A perfectly elastic demand curve is parallel to the X-axis. Why or why not?
What is price elasticity of demand for life saving drugs?
Why is market demand curve more elastic than an individual demand curve?
Price elasticity of demand of good X is −2 and of good Y is −3. Which of the two goods has more price elasticity and why?
Arrange the following coefficients of price elasticity of demand in ascending order.
−0.87, −0.53, −31 , −0.80
What will be the effect of 10 percent rise in price of a good on its demand if price elasticity of demand is zero?
What will be the effect of 10 percent rise in price of a good on its demand if price elasticity of demand is −1?
What will be the effect of 10 percent rise in price of a good on its demand if price elasticity of demand is −2?
Indicate the degree of elasticity of demand of the following demand curve.
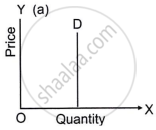
Indicate the degree of elasticity of demand of the following demand curve.
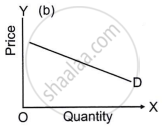
State 3 factors which affect price elasticity of demand.
Draw a diagram showing the Elasticity of demand less than one.
Draw a diagram showing a perfectly elastic demand curve.
Explain the different types of price elasticity of demand.
What is the price elasticity of demand for the following demand curve:
Straight line demand curve parallel to X-axis.
What is the price elasticity of demand for the following demand curve:
Straight line demand curve parallel to Y-axis.
What is the price elasticity of demand for the following demand curve:
Rectangular hyperbola.
The nature of a commodity determines its price elasticity of demand. Explain.
How is the price elasticity of demand of a commodity is affected by the number of its substitutes.
Discuss any three/ four factors determining price elasticity of demand.
Study the statement given below and state whether demand will be elastic or inelastic, citing reasons for your answer.
Demand for cigarettes by a habitual smoker.
Study the statement given below and state whether demand will be elastic or inelastic, citing reasons for your answer.
A consumer postpones the purchase of a refrigerator till the off-season sale.
State the formula for calculating the price elasticity of demand using the percentage method.
State whether demand for the following goods is elastic or inelastic?
- car
- textbooks
- cigarettes
- diamonds
- milk
- seasonal vegetables
- coal
- Dawat basmati rice
- needles
- colour T.V.
From the following state whether the price elasticity of demand is inelastic, relatively elastic, highly elastic or highly inelastic. Give reasons to support your answer.
demand for school uniform
From the following state whether the price elasticity of demand is inelastic, relatively elastic, highly elastic or highly inelastic. Give reasons to support your answer.
demand for refrigerators
From the following state whether the price elasticity of demand is inelastic, relatively elastic, highly elastic or highly inelastic. Give reasons to support your answer.
demand for electricity
From the following state whether the price elasticity of demand is inelastic, relatively elastic, highly elastic or highly inelastic. Give reasons to support your answer.
demand for cigar by a chain smoker
From the following state whether the price elasticity of demand is inelastic, relatively elastic, highly elastic or highly inelastic. Give reasons to support your answer.
demand for diesel and petrol
From the following state whether the price elasticity of demand is inelastic, relatively elastic, highly elastic or highly inelastic. Give reasons to support your answer.
demand for personal computers
From the following state whether the price elasticity of demand is inelastic, relatively elastic, highly elastic or highly inelastic. Give reasons to support your answer.
Demand for precious stones and costly jewellery
Define income elasticity of demand.
Define or explain the following concept:
Cross Elasticity of Demand
Solutions for 2: Elasticity of Demand
![Goyal Brothers Prakashan solutions for Economic Application [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 2 - Elasticity of Demand Goyal Brothers Prakashan solutions for Economic Application [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 2 - Elasticity of Demand - Shaalaa.com](/images/economic-application-english-class-10-icse_6:4ae302fabf354f56a3e776b0889e746c.jpg)
Goyal Brothers Prakashan solutions for Economic Application [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 2 - Elasticity of Demand
Shaalaa.com has the CISCE Mathematics Economic Application [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Goyal Brothers Prakashan solutions for Mathematics Economic Application [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE 2 (Elasticity of Demand) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Goyal Brothers Prakashan textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Economic Application [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 2 Elasticity of Demand are Elasticity of Demand, Types of Elasticity of Demand, Degrees of Elasticity of Demand, Methods of Measuring Price Elasticity of Demand, Factors Affecting Price Elasticity of Demand.
Using Goyal Brothers Prakashan Economic Application [English] Class 10 ICSE solutions Elasticity of Demand exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Goyal Brothers Prakashan Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CISCE Economic Application [English] Class 10 ICSE students prefer Goyal Brothers Prakashan Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 2, Elasticity of Demand Economic Application [English] Class 10 ICSE additional questions for Mathematics Economic Application [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
