Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
▶ 1: Elementary Theory of Demand
2: Elasticity of Demand
3: Theory of Supply
Unit II - Factors of Production : Basic Concepts
4: Factors of Production
Unit III - Alternative Market Structures : Basic Concepts
5: Nature and Structure of Markets
Unit IV - The State and Economic Development
6: The State and Economic Development
Unit V - Money and Banking : Basic Concepts
7: Meaning and Functions of Money
8: Commercial Banks
9: Central Banks
10: Inflation
![Goyal Brothers Prakashan solutions for Economic Application [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 1 - Elementary Theory of Demand Goyal Brothers Prakashan solutions for Economic Application [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 1 - Elementary Theory of Demand - Shaalaa.com](/images/economic-application-english-class-10-icse_6:4ae302fabf354f56a3e776b0889e746c.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 1: Elementary Theory of Demand
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 1 of CISCE Goyal Brothers Prakashan for Economic Application [English] Class 10 ICSE.
Goyal Brothers Prakashan solutions for Economic Application [English] Class 10 ICSE 1 Elementary Theory of Demand QUESTIONS [Pages 16 - 23]
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
______ means a wish to have a commodity or source.
Want
Demand
Effective desire
Desire
Which of the following statement is not true?
Want is an effective desire
Demand is different from want
Demand is always at a price
In economics, the terms - 'desire' 'want' and 'demand' have the same meanings.
Any statement about demand for a good is considered complete only when the following is/are mentioned in it:
Price of the good
Quantity of the good
Period of time
All of the above
Which of the following is not a determinant of demand?
Income of the consumer
Price of the product
Price of related goods
Technology used to produce the goods
Size of population
The demand curve is generally ______.
downward sloping
upward sloping
horizontal parallel to the X-axis
vertical parallel to the Y-axis
Following is not the assumption of law of demand:
Commodity's own price should remain constant.
Income of the consumers should remain constant.
Price of related good should not change.
There should be no change in consumer's tastes an preference.
If due to fall in the price of good X, demand for Y rises, the two goods are ______.
Substitutes
Complements
Not related
Competitive
What kind of a commodity will have inverse relation between income and demand?
Normal good
Inferior good
Essential good
Luxury good
With an increase in income, the consumption of which good, the consumer reduces ______.
Inferior good
Normal goods
Both (a) and (b)
Neither (a) nor (b)
If with the rise in price of good Y, demand for good X rises, the two goods are:
Substitutes
Complements
Not related
Jointly
What does a downward movement along the same demand curve indicate?
Increase in demand
Decrease in demand
Contraction in demand
Expansion in demand
What does an upward movement along the same demand curve indicate?
Increase in demand
Decrease in demand
Contraction in demand
Expansion in demand
When the demand curve of a product shifts to the right, it represents a situation of ______.
Increase in demand
Expansion in demand
Decrease in demand
Contraction in demand
An increase in the price of electricity, will curve the demand for electric appliances to ______.
rise
fall
remain the same
None of these
When at a price of ₹ 5 per unit of a commodity, A's demand is for 11 units, B's demand is for 14 units and C's demand is for units (assuming that there are only three consumers in the market), the market demand is ______.
11 units
14 units
17 units
33 units
Demand schedule is a list of prices and quantities.
True
False
Giffen goods are richman's goods
True
False
From the following data regarding individual demand schedules of households A, B and market demand schedule, what will be the values of (i) and (ii) (Assuming that there are only 2 households in the market).
| Price (in ₹) | Individual Demand (units) | Market demand (units) | ||
| A | B | C | ||
| 7 | (i) | 16 | 15 | 51 |
| 8 | 18 | 15 | (ii) | 46 |
| 9 | 16 | 12 | 11 | 39 |
| 10 | 13 | 10 | 9 | 32 |
18, 13
13, 20
20, 13
13, 18
Demand for milk is an example of composite demand.
True
False
Which of the following is not a determinant of demand?
Income of the consumer
Price of the product
Price of related goods
Technology used to produce the goods
Size of population
The market demand curve is a ______ summation of all Individual demand curves:
Vertical
Lateral
Downward
None of the above
The goods whose demand decreases as income increases.
Luxuries
Giffen goods
Inferior goods
Necessities
Mr Vijay purchases 2 litres of milk per day when it is priced at ₹ 35 per litre. Suppose he has some guests at home and consequently he purchases 6 litres of milk on that day. What will you call it?
Increase in demand
Increase in quantity demanded
What will be the values of (i) and (ii)?
| Price (in ₹) | Quantity Demanded by | Total Demand | ||
| A | B | C | ||
| 10 | 30 | (i) | 12 | 52 |
| 20 | 20 | 8 | 9 | 37 |
| 30 | 10 | 6 | (ii) | 22 |
10 and 12
6 and 10
10 and 6
6 and 12
Match the following and select the correct option.
| Column A | Column B | ||
| (i) | Extention of demand | A. | Prices are expected to rise in future |
| (ii) | Decrease in demand | B. | Rise in price |
| (iii) | Contraction of demand | C. | Prices are expected to fall in future |
| (iv) | Increase in demand | D. | Fall in prices |
(i) D, (ii) C, (iii) B, (iv) A
(i) B, (ii) C, (iii) A, (iv) D
(i) C, (ii) A, (iii) B, (iv) A
(i) D, (ii) C, (iii) A, (iv) B
If X and Y are complementary goods, a rise in the price of Y will cause the demand curve of X to ______.
Shift to the left
Shift to the right
Extend
Contract
An increase in the price of electricity will cause an ______.
Increase in the demand for solar heaters
Decrease the demand for solar heaters
Increase in the demand for Geysers
None of the above
| Price in (₹) | Quantity demanded (units) |
| 20 | 100 |
| 25 | 70 |
The above example represents a situation of ______.
Increase in demand
Decrease in demand
Contraction of demand
Extention of demand
From the given demand schedule, what will be the effect on demand curve.
| Price in (₹) | Demand (units) |
| 20 | 100 |
| 20 | 70 |
Shift to right
Shift to left
Upward movement along the demand curve
Downward movement along the demand curve
If prices of cars rise, many people may put off buying a new car. So the demand for petrol will fall.
True
False
If a good is inferior good, then purchases of that good will decrease when ______.
The supply of it increases
Population increases
Income increases
The price of a substitute rises
Goods X and Y are complements when they are ______.
Used together to satisfy a want
X is of better quality than Y
Used instead of each other
X is of inferior quality compared to Y
Individual demand is a demand by a single buyer.
True
False
Pick the option which does not belong to the group:
Digital watches
Nuclear weapons
Soaps
Smart phones
The graphical representation of total demand in an economy y is a ______.
Individual demand curve
Market demand curve
Market demand schedule
Composite demand schedule
What does the graph below indicate?
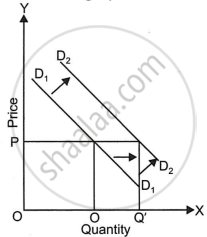
Increase in quantity demanded
Decrease in quantity demanded
Increase in demand
Decrease in demand
The demand for a Good X increases when the price of its substitute ______ OR when the price of its complements ______.
rises: rise
rises: falls
falls: rises
falls: falls
The Law of Demand shows the relationship between ______.
income and price
price and quantity demanded
income and quantity demanded
quanitity demanded and quantity supplied
Identity the pair of goods which are substitutes of each other:
Coffee and sugar
Tea and coffee
Bread and butter
Pen and ink
Which of these is NOT an assumption of the Law of Demand?
No change in the consumer's income
Consumers do not expect any change in the price of the commodity in the near future
The price of substitute remains constant
The number of firms supplying the commodity does not change
The demand curve which indicates the inverse relationship between price and demand ______.
Slopes upward
Slopes downward
Remains horizontal
Remains vertical
If tea and coffee are substitutes, then bread and butter are examples of ______.
Joint goods
Similar goods
Complementary goods
Homogeneous goods
Mobile phones and SIM cards are examples of ______.
Substitute goods
Complementary goods
Unrelated goods
Competitive goods
Assertion-Reasoning & Matching Based Questions
Assertion (A): The statement 'A consumer buys 2 litres of milk everyday at a price of ₹50 per litre of milk' is demand statement.
Reason (R): The demand for a commodity is always expressed with references to price and time.
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Assertion (A) is true but Reason (R) is false.
Assertion (A) is false but Reason (R) is true.
Assertion (A): If the income of a consumer increases, other things constant, the demand curve for a normal goods shifts to the right.
Reason (R): As income increases, the demand curve for an inferior good shifts to the left.
As income increases, the demand curve for an inferior shifts to the left.
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Assertion (A) is true but Reason (R) is false.
Assertion (A) is false but Reason (R) is true.
Assertion (A): Demand curve is downward sloping.
Reason (R): Demand curve slopes downwards from left to the right because price and quantity demanded are inversely related.
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Assertion (A) is true but Reason (R) is false.
Assertion (A) is false but Reason (R) is true.
Match the following:
| Column I | Column II |
| A. Extension of demand. | (i) A larger quantity is demanded at the same price. |
| B. Contraction of demand. | (ii) A smaller quantity is demanded at the same price. |
| C. Increase in demand. | (iii) Fall in quantity demanded due to the rise in its price. |
| D. Decrease in demand | (iv) Rise in the quantity demanded of a commodity as a result of fall in the price. |
A. (i), B. (iv), C. (ii)
A. (iv), B. (iii) C. (ii), D. (v)
A (iv), B. (iii), C. (i) D. (ii)
A. (iv), B. (ii), C. (iii), D. (ii)
From the set of statements given in Column I and Column II, choose the correct pair of statements:
| Column I | Column II |
| A. Normal goods | (i) Goods the demand for which tends to fall with increase in income. |
| B. Inferior goods | (ii) Goods which cannot be used in place of one another. |
| C. Substitute goods | (iii) Goods which can be used in place of one another. |
| D. Joint demand | (iv) Goods the demand for which rise with increase in income. |
A. (iv), B. (i), C. (ii) D. (iii)
A. (iii), B. (ii) c. (iv), D. (i)
A (ii), B. (i), c. (iii), D. (iv)
A. (iv), B. (i), C. (iii), D. (ii)
Short Answer Type Questions
Define the term demand.
Draw a neat labelled diagram of a demand curve.
State two important determinants of demand.
What are inferior goods?
Give an example of inferior goods.
What do you mean by substitute goods?
Give two examples of substitute goods.
What do you mean by complementary goods?
What do you mean by complementary goods?
Give two examples of complementary goods.
Explain the impact on demand of complementary goods.
If price of X increases, then demand for Y too increases. What is the relationship between goods X and Y? Give an example.
If the quantity demanded of commodity X decreases as the householder's income increases. What type of a commodity is X? Give an example.
How does an increase in income affect the demand for a normal good?
Give the meaning of joint demand.
Distinguish between derived demand and composite demand.
Differentiate between Giffen goods and inferior goods.
State the law of demand.
What are the assumptions of the Law of Demand?
What is meant by the income effect of a fall in the prices of a commodity?
With the help of a suitable example explain the effect of a rise in price on the demand for complementary goods.
Construct a demand schedule showing relationship between price and quantity demanded.
Mention one exception to the law of demand. Give one point only.
Explain the term 'Veblen effect'. Give an example.
What does the demand curve given below show?
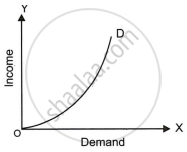
With the help of a suitable diagram explain the extension in demand?
What is contraction in demand?
What is increase in demand?
What is decrease in demand?
Differentiate between a change in quantity demanded and a change in demand.
Explain the following diagram:
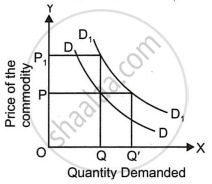
The following table shows a change in the demand. Read the table carefully and answer the question that follows:
| Case | Price (₹) | Quantity (kg) |
| I | 10 | 20 |
| 10 | 10 | |
| II | 10 | 20 |
| 5 | 20 |
What type of change is it - decrease in demand or contraction in demand? Give a reason.
Give two reasons for the shift of the demand curve towards the left.
Give two reasons for the shift of the demand curve towards the right.
In 2002, the prices of gold nearly tripled. yet, as the price of gold rose its sales too increased. Does this mean that the demand curve for gold is upward sloping? Justify your answer.
In order to encourage tourism in Goa, Government of India suggests to Indian Airlines to reduce air fare to Goa from four major cities - Chennai, Kolkata, Mumbai and New Delhi. If the Indian Airlines reduces the air fare to Goa, how will this affect the market demand curve for air travel to Goa?
There are train and bus services between New Delhi and Jaipur. Suppose, the train fare between the two cities comes down. How will this affect the demand curve for bus travel between the two cities?
Draw a demand curve on the basis of the following data.
| Price per unit (₹) | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| Quantity demanded (Units) | 1000 | 800 | 700 | 600 | 500 | 200 |
Shyam, Sita, Renu, Ahmed and John are five consumers of apples. Their demand for apples is given below. Derive the market demand schedule for apples.
| Price per Kg. (In ₹) | Quantity Demanded (Apples) in Kg. | ||||
| Shyam | Sita | Renu | Ahmed | John | |
| 25.00 | 16 | 15 | 12 | 14 | 18 |
| 30.00 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 8 | 15 |
| 35.00 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 6 | 12 |
| 40.00 | 8 | 6 | 4 | 2 | 8 |
Complete the following individual demand schedule.
| Price in (₹) | Quantity of sugar Demanded in Kgs |
| 5 | 20 |
| 6 | ______ |
| 7 | ______ |
| 8 | ______ |
| 9 | ______ |
Distinguish between derived demand and composite demand.
Long Answer Type Questions
Define the term demand.
Explain briefly the factors which influence individual demand for a commodity.
Define composite demand.
Explain any three determinants of market demand.
Define the term demand.
Explain how quantity demanded for commodity X will be affected by An increase in the price of its substitute.
Explain how quantity demanded for commodity X will be affected by Consumer credit facility.
Explain how quantity demanded for commodity X will be affected by Government policy.
State and explain the law of demand with the help of a hypothetical schedule and graph.
What are the assumptions of the Law of Demand?
Mention one exception to the law of demand. Give one point only.
State the law of demand.
Mention one exception to the law of demand. Give one point only.
Explain four circumstances under which the law of demand does not operate.
“The inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded does not hold good in many cases.”
- Justify the above as Yes or No.
- If justified, explain in brief the Giffen Effect.
What are the assumptions of the Law of Demand?
State and explain the law of demand with the help of a hypothetical schedule and graph.
How does demand differ from want?
Give the meaning of joint demand.
Distinguish between Individual demand and Market demand.
Does a demand curve always have a negative slope? Give three reasons to justify your answer.
Goyal Brothers Prakashan solutions for Economic Application [English] Class 10 ICSE 1 Elementary Theory of Demand QUESTION BANK [Pages 23 - 28]
Define the term demand.
Define individual demand.
Define market demand.
Define the term demand.
State two factors affecting the market demand for a commodity.
State two types of related goods.
What do you mean by substitute goods?
Give two examples of substitute goods.
Define complementary goods.
Give two examples of complementary goods.
What do you mean by a normal good?
What are inferior goods?
Give an example of inferior goods.
What are Giffen goods?
Give an example of Giffen goods.
What are Veblen goods?
Given an example of Veblen goods.
What is demand function?
State the law of demand.
What is meant by expansion of demand?
What is increase in demand?
What is contraction in demand?
What is decrease in demand?
What causes a downward movement along a demand curve?
What causes an upward movement along a demand curve?
What does a rightward shift of demand curve indicate?
Mention one exception to the law of demand. Give one point only.
State two circumstances under which the demand curve slopes upwards to the right.
What is a demand schedule?
What is meant by the income effect of a fall in the prices of a commodity?
Define the term demand.
Explain any four factors affecting the demand for a commodity.
With the help of a diagram, show how a market demand curve can be obtained from individual demand curves.
Draw a demand curve with the help of a hypothetical individual demand schedule.
State the law of demand.
Briefly explain any three determinants for the negative slope of the demand curve.
What are the assumptions of the Law of Demand?
Explain four circumstances under which the law of demand does not operate.
Explain the diagram given alongside.
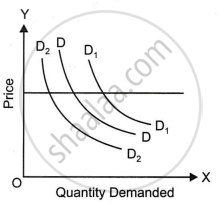
Differentiate between a change in quantity demanded and a change in demand.
The following table shows a change in the demand. Read the table carefully and answer the question that follows:
| Case I | Case II | ||
| Price (₹) | Quantity | Price (₹) | Quantity |
| 10 | 20 | 10 | 20 |
| 10 | 10 | 5 | 20 |
What type of change is it, decrease in demand or contraction in demand? Give a reason.
With the help of a suitable diagram explain the extension in demand?
Explain the following diagram:

Give the meaning of Price demand.
Give the meaning of Income demand.
Give the meaning of Cross demand.
Distinguish between Joint demand and Composite demand.
Give one point each of similarity and dissimilarity between Giffen goods and Veblen goods.
Does a demand curve always have a negative slope? Give three reasons to justify your answer.
Solutions for 1: Elementary Theory of Demand
![Goyal Brothers Prakashan solutions for Economic Application [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 1 - Elementary Theory of Demand Goyal Brothers Prakashan solutions for Economic Application [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 1 - Elementary Theory of Demand - Shaalaa.com](/images/economic-application-english-class-10-icse_6:4ae302fabf354f56a3e776b0889e746c.jpg)
Goyal Brothers Prakashan solutions for Economic Application [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 1 - Elementary Theory of Demand
Shaalaa.com has the CISCE Mathematics Economic Application [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Goyal Brothers Prakashan solutions for Mathematics Economic Application [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE 1 (Elementary Theory of Demand) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Goyal Brothers Prakashan textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Economic Application [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 1 Elementary Theory of Demand are Concept for Demand, Types of Demand, Law of Demand, Assumptions of Law of Demand, Demand Schedule, Demand Curve, Determinants of Demand Or Demand Function, Exceptions to the Law of Demand, Movement Along and Shifts in the Demand Curve, Shift in Demand Curve.
Using Goyal Brothers Prakashan Economic Application [English] Class 10 ICSE solutions Elementary Theory of Demand exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Goyal Brothers Prakashan Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CISCE Economic Application [English] Class 10 ICSE students prefer Goyal Brothers Prakashan Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 1, Elementary Theory of Demand Economic Application [English] Class 10 ICSE additional questions for Mathematics Economic Application [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
