Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
How does an increase in income affect the demand for a normal good?
Solution
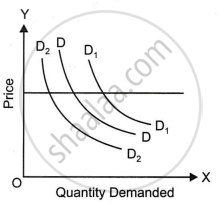
Normal goods are those for which demand increases as consumers' income rises. When people have more income, they spend more on goods and services that improve their quality of life or satisfy their desires more fully.
Impact on Demand:
- Rightward Shift in the Demand Curve: As income increases, the demand for normal goods rises at each price level. This causes the entire demand curve for the normal good to shift to the right, indicating a higher quantity demanded at every price.
- Examples of Normal Goods:
- Clothing: As income increases, people may buy more or better-quality clothing.
- Dining Out: With more disposable income, people may choose to dine out more frequently or at more expensive restaurants.
- Electronics: Higher income might lead to increased spending on better or more advanced electronic devices.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
An increase in the price of electricity, will curve the demand for electric appliances to ______.
The goods whose demand decreases as income increases.
Mr Vijay purchases 2 litres of milk per day when it is priced at ₹ 35 per litre. Suppose he has some guests at home and consequently he purchases 6 litres of milk on that day. What will you call it?
If X and Y are complementary goods, a rise in the price of Y will cause the demand curve of X to ______.
Match the following:
| Column I | Column II |
| A. Extension of demand. | (i) A larger quantity is demanded at the same price. |
| B. Contraction of demand. | (ii) A smaller quantity is demanded at the same price. |
| C. Increase in demand. | (iii) Fall in quantity demanded due to the rise in its price. |
| D. Decrease in demand | (iv) Rise in the quantity demanded of a commodity as a result of fall in the price. |
Differentiate between a change in quantity demanded and a change in demand.
The following table shows a change in the demand. Read the table carefully and answer the question that follows:
| Case | Price (₹) | Quantity (kg) |
| I | 10 | 20 |
| 10 | 10 | |
| II | 10 | 20 |
| 5 | 20 |
What type of change is it - decrease in demand or contraction in demand? Give a reason.
There are train and bus services between New Delhi and Jaipur. Suppose, the train fare between the two cities comes down. How will this affect the demand curve for bus travel between the two cities?
What does a rightward shift of demand curve indicate?
Explain the diagram given alongside.