Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Explain Kolbe’s reaction.
Solution
Kolbe’s (or) Kolbe’s Schmit reaction:
In this reaction, phenol is first converted into sodium phenoxide which is more reactive than phenol towards electrophilic substitution reaction with CO2. Treatment of sodium phenoxide with CO2 at 400 K, 4-7 bar pressure followed by acid hydrolysis gives salicylic acid.
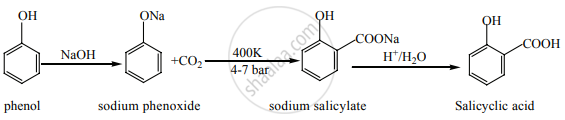
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Which of the following compounds on reaction with methyl magnesium bromide will give tertiary alcohol.
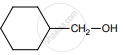 on treatment with Con. H2SO4 predominately gives
on treatment with Con. H2SO4 predominately gives
\[\ce{(CH3)3 - C - CH(OH) CH3 ->[con H2SO4] X (major product)}\]
Arrange the following in the increasing order of their boiling point and give a reason for your ordering.
Propan-1-ol, propan-1, 2, 3-triol, propan-1, 3-diol, propan-2-ol
Can we use nucleophiles such as NH3, CH3O for the Nucleophilic substitution of alcohols?
Draw the major product formed when 1-ethoxyprop-1-ene is heated with one equivalent of HI
Predict the major product, when 2-methyl but -2-ene is converted into an alcohol in each of the following method.
Acid catalysed hydration
Predict the major product, when 2-methyl but -2-ene is converted into an alcohol in the following method.
Acid catalysed hydration
What will be the product (X and A)for the following reaction
\[\ce{acetylchloride ->[i) CH3MgBr][ii) H3O] X ->[acid K2Cr2O7] A}\]
What will be the product (X and A) for the following reaction.
\[\ce{acetylchloride ->[i) CH3MgBr][ii) H3O^+] X ->[acid K2Cr2O7] A}\]
