Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Explain sclereids with their types.
Solution
Sclereids are dead cells, usually these are isodiametric but some are elongated too. The cell wall is very thick due to lignification. Lumen is very much reduced. The pits may simple or branched. Sclereids are mechanical in function. They give hard texture to the seed coats, endosperms etc., Sclereids are classified into the following types.
- Branchysclereids or Stone cells: Isodiametric sclereids, with hard cell wall. It is found in bark, pith cortex, hard endosperm and the fleshy portion of some fruits.
eg: Pulp of Pyrus. - Macrosclereids: Elongated and rod shaped cells, found in the outer seed coat of leguminous plants. eg: Crotalaria and Pisum sativum.
- Osteosclereids (Bone cells): Rod shaped with dilated ends. They occur in leaves and seed coats.
eg: seed coat of Pisum and Hakea. - Astrosclereids: Star cells with lobes or arms diverging form a central body. They occur in petioles and leaves.
eg: Tea, Nymphae and Trochodendron. - Trichosclereids: Hair like thin-walled sclereids. Numerous small angular crystals are embedded in the wall of these sclereids, present in stems and leaves of hydrophytes.
eg: Nymphaea leaf and Aerial roots of Monstera.
RELATED QUESTIONS
What are the functions of the stomata?
Name the tissue that transports food in plants.
What is the role of epidermis in plants?
Draw a well labelled diagram of xylem.
What are tracheary elements? Describe their functions.
What are the functions of phloem?
What is simple tissue? Classify and explain its different types with suitable diagram.
Study the diagram given below and then answer the question that follows:
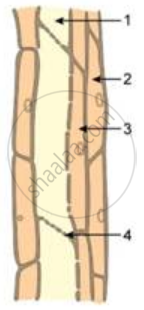
Where is this tissue likely to be found in the plant?
Study the diagram given below and then answer the question that follows:
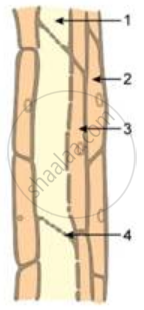
State the function of the parts labelled 1, 2, 3 and 4.
Differentiate between:
Parenchyma and collenchyma
Name the tissue associated with the following:
Movement of food in the plant body
The question has four answers. Choose the correct answer:
The parenchymatous tissue is
Write a short note on peculiarity of a sclerenchyma cell wall.
Differentiate between Xylem and Phloem functioning
Distinguish Between Internal or anatomical difference between monocots and dicots.
While doing work and running, you move your organs like hands, legs, etc. Which among the following is correct?
Match the column (A) with the column (B)
| (A) | (B) | ||
| (a) | Parenchyma | (i) | Thin walled, packing cells |
| (b) | Photosynthesis | (ii) | Carbon fixation |
| (c) | Aerenchyma | (iii) | Localized thickenings |
| (d) | Collenchyma | (iv) | Buoyancy |
| (e) | Permanent tissue | (v) | Sclerenchyma |
Name the two types of sclerenchyma cells.
Differentiate fibers from sclereids.
