Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Explain the application of heating effect of electric current in an electric bulb with a diagram.
Solution
- Electric bulb works on the principle of heating effect electric of current.
- The solenoid type coil of bulb has high resistivity and very high melting point.
- When current is passed through the bulb, solenoid type coil of bulb gets heated to high temperature (upto 3400 °C) and starts glowing.

RELATED QUESTIONS
Write Joule's law of heating.
An electric heater is connected to the 230 V mains supply. A current of 8 A flows through the heater.
(b) How much energy is transferred to the heater each second?
Give two reasons why nichrome alloy is used for making the heating elements of electrical appliances.
Why does the connecting cord of an electric heater not glow hot while the heating element does?
An electric iron of resistance 20 ohms draws a current of 5 amperes. Calculate the heat produced in 30 seconds.
Derive the expression for the heat produced due to a current 'I' flowing for a time interval 't' through a resistor 'R' having a potential difference 'V' across its ends. With which name is this relation known?
What is meant by the heating effect of current? Give two applications of the heating effect of current.
The current passing through an electric kettle has been doubled. The heat produced will become:
(a) half
(b) double
(c) four time
(d) one-fourth
An electric fuse works on the:
(a) chemical effect of current
(b) magnetic effect of current
(c) lighting effect of current
(d) heating effect of current
An electric iron is connected to the mains power supply of 220 V. When the electric iron is adjusted at 'minimum heating' it consumes a power of 360 W but at 'maximum heating' it takes a power of 840 W. Calculate the current and resistance in each case.
Give a scientific reason.
Tungsten metal is used to make a solenoid type coil in an electric bulb.
Give a scientific reason.
For electric power transmission, copper or aluminium wire is used.
Identify the figure and give its use.

Give scientific reason :
In the electric equipment producing heat e.g. iron, electric heater, boiler, toaster, etc., an alloy such as Nichrome is used, not pure metals.
Name the factors on which the heat produced in a wire depends when current is passed in it, and state how does it depend on the factors stated by you.
Rewrite the following statement by selecting the correct option:
1 A = ____________ mA.
Solve the following question.
Compute the heat generated while transferring 96000 coulombs of charge in two hours through a potential difference of 40 V.
Find the odd one out and give its explanation.
Which metal is used to make the filament of an electric bulb?
Write scientific reason.
A coil made up of alloy Nichrome is used in the electric heater cooker as a resistor.
True or False – If False give the correct answer
The fuse wire does not melts whenever there is overload in the wiring.
Which of the following is correct?
A current of 1 A is drawn by a filament of an electric bulb. Number of electrons passing through a cross-section of the filament in 16 seconds would be roughly:
The heating element of an electric iron is made up of:
Which of the following gases are filled in electric bulbs?
What is Joule’s heating effect? How can it be demonstrated experimentally? List its four applications in daily life.
(a) Observe the diagram given below and state whether the bulb will glow or not when we switch on K.
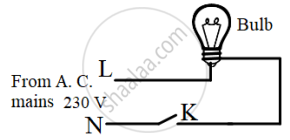
(b) Is it safe to handle the bulb when the switch is OFF?
(c) Give a reason for your answer in (b).
When a switch is in the OFF position,
(i) circuit starting from the positive terminal of the cell stops at the switch.
(ii) circuit is open.
(iii) no current flows through it.
(iv) current flows after some time. Choose the combination of the correct answers from the following.
Your teacher has shown you the following activity.

Activity: The teacher has wound a long insulated piece of wire around an iron nail in the form of a coil. The free ends of the wire are connected to a cell through a switch as shown in Figure 14.3. The current is switched on and some pins are placed near the ends of the nail.
Write down any three questions that come to your mind about this activity
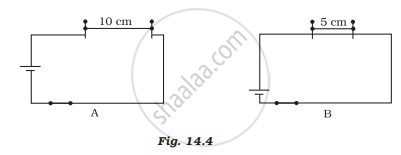
Paheli took a wire of length of 10 cm. Boojho took a wire of 5 cm of the same material and thickness. Both of them connected the wires as shown in the circuit given in Figure 14.4. The current flowing in both circuits is the same.
(i) Will the heat produced in both cases be equal? Explain
(ii) Will the heat produced be the same if the wires taken by them are of equal lengths but of different thicknesses? Explain.
Copper wire offers very little ______ and does not get heated up quickly.
Name the effect of the current responsible for the glow of the bulb in an electrical circuit.
The following is not a safety device.
An electric fuse is a wire made up of a material having ______ melting point.
The electric fuse works on the Joule heating principle.
Find the odd one out.
Two students decided to investigate the effect of water and air on iron object under identical experimental conditions. They measured the mass of each object before placing it partially immersed in 10 ml of water. After a few days, the object were removed, dried and their masses were measured. The table shows their results.
| Student | Object | Mass of Object before Rusting in g |
Mass of the coated object in g |
| A | Nail | 3.0 | 3.15 |
| B | Thin plate | 6.0 | 6.33 |
What might be the reason for the varied observations of the two students?
In which of the following applications of Iron, rusting will occur most? Support your answer with valid reason.
| A | B | C | D |
 |
 |
 |
 |
In a set up the students coated iron nails with zinc metal and noted that, iron nails coated with zinc prevents rusting. They also observed that zinc initially acts as a physical barrier, but an extra advantage of using zinc is that it continues to prevent rusting even if the layer of zinc is damaged. Name this process of rust prevention and give any two other methods to prevent rusting.
