Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Explain the following reaction.
Silicon is heated with methyl chloride at high temperature in the presence of copper.
Solution
When silicon reacts with methyl chloride in the presence of copper (catalyst) and at a temperature of about 537 K, a class of organosilicon polymers called methyl-substituted chlorosilanes (MeSiCl3, Me2SiCl2, Me3SiCl, and Me4Si) are formed
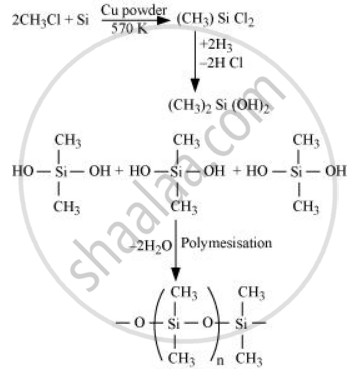
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Discuss the pattern of variation in the oxidation states of B to Tl.
Discuss the pattern of variation in the oxidation states of C to Pb.
Explain why is there a phenomenal decrease in ionisation enthalpy from carbon to silicon?
Write suitable chemical equations to show the nature of the following oxide.
Tl2O3
Rationalise the given statement and give a chemical reaction:
Lead (IV) chloride is highly unstable towards heat.
Rationalise the given statement and give a chemical reaction:
Lead is known not to form an iodide, PbI4.
Classify the following oxide as neutral, acidic, basic or amphoteric:
CO
Classify the following oxide as neutral, acidic, basic or amphoteric:
B2O3
Classify the following oxide as neutral, acidic, basic or amphoteric:
CO2
Classify the following oxide as neutral, acidic, basic or amphoteric:
PbO2
Write suitable chemical equations to show the nature of the following oxide.
B2O3
Write suitable chemical equations to show the nature of the following oxide.
SiO2
Catenation i.e., linking of similar atoms depends on size and electronic configuration of atoms. The tendency of catenation in Group 14 elements follows the order:
Explain the following:
Silicon forms \[\ce{SiF^{2-}6}\] ion whereas corresponding fluoro compound of carbon is not known.
The +1 oxidation state in group 13 and +2 oxidation state in group 14 becomes more and more stable with increasing atomic number. Explain.
Explain the following:
BF3 does not hydrolyse.
Explain the following:
Why does the element silicon, not form a graphite like structure whereas carbon does.
