Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Explain the formation of placenta after the implantation in a human female.
Solution
The placenta, which supplies nutrition to the developing foetus, is a unique characteristic of placental mammals. The placenta, which serves as a structural and functional link between the developing embryo (foetus) and the mother's body, develops between the chorionic villi and uterine tissue after around 12 weeks of pregnancy. Upon the implantation of a blastocyst in the mother's endometrium, the placenta starts to grow. Two different cell types make up the blastocyst: the inner cell mass and the outer trophoblast cells. The trophoblast cells grow to create the placenta, while the inner cell mass gives rise to the foetus and the protective barrier around it. Between 18 and 20 weeks of pregnancy, the placenta is developed, and it keeps expanding. A chorio-allantoic placenta is one that develops from the chorion and allantois in the human placenta. The placenta protects the foetus from the typical immune reaction that releases antibodies, even though the mother's body may perceive it as a foreign body.
RELATED QUESTIONS
Eye lens is formed from ______.
Which extra-embryonic membrane in humans prevents desiccation of the embryo inside the uterus?
Urine test during pregnancy determines the presence of ______.
The early stage human embryo distinctly possesses ______.
Relaxin is the hormone secreted by the placenta.
The concentration of which of the following substances will decrease in the maternal blood as it flows from embryo to placenta through the umbilical cord?
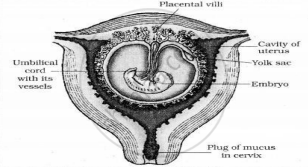
The human foetus within the uterus
- Oxygen
- Amino Acids
- Carbon dioxide
- Urea
Which of the following is not a function of the placenta?
Read the following and answer from given below:
Cleavage is the series of rapid mitotic divisions in the zygote and forms blastula. The 2, 4, 8, 16 daughter cells are called blastomeres. An embryo with 64 blastomeres is known as a blastocyst and has a blastocoel cavity. Blastocyst gets implanted in the uterine wall and leads to pregnancy.
At which stage of embryonic development does trophectoderm develop?
The secondary sexual characters develop in females because:
Match the columns I and II with reference to weeks of pregnancy and the development of a human embryo. Select the correct option from the choices given below:
| Column I | Column II | ||
| I. | 8 weeks | (P) | Limbs and external genital organs |
| II. | 12 weeks | (Q) | Limbs and digits develop. |
| III. | 20 weeks | (R) | Body hair develops. |
| IV. | 24 weeks | (S) | Eyelids separate. |
