Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
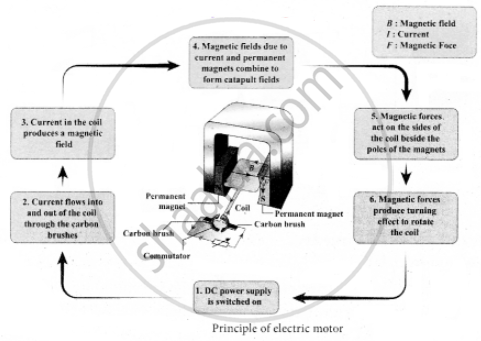
Explain the principle, construction and working of a dc motor.
Solution
A motor is an electrical machine which converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. The principle of working of a DC motor according to Faraday’s laws of electromagnetic induction is that “whenever a current carrying conductor is placed in a magnetic field, it experiences a mechanical force”. The various parts of a DC motor are; Permanent magnets on both sides of a coil which consists of carbon brush and commutator as shown in

Working of electric motor is primarily dependent upon the interaction between magnetic field and current. The direction of this force is given by Fleming’s left hand rule and it’s magnitude is given by F = BIL. Where, B = magnetic flux density, I = current and L = length of the conductor within the magnetic field.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
State Faraday's laws of electromagnetic induction.
State Lenz's Law.
In the following diagram an arrow shows the motion of the coil towards the bar magnet.
(1) State in which direction the current flows, A to B or B to A?
(2) Name the law used to come to the conclusion.

A conductor is moved in a varying magnetic field. Name the law which determines the direction of current induced in the conductor.
The instantaneous magnetic flux in a circuit is `phi=4t^2-4t+1`. The total resistance of circuit is 15 Ω. At t = 2s, the induced current in circuit is ____________.
A coil of 25 turns is pulled in 0.05 s between the poles of a magnet, where its area includes `21 xx106-6 "Wb" "to" 1 xx 10^-6 "Wb"`. The average e.m.f. is ______.
The direction of the magnetic field around a straight conductor carrying current can be determined by ______.
The laws of induction were given by ______.
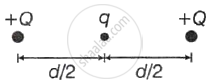
Two positively charged particles each having charge Q and are d distance apart. A third charge is introduced in midway on the line joining the two. Find nature and magnitude of third charge, so that the system is in equilibrium ______.
Express Faraday-Lenz's law of electromagnetic induction in an equation form.
