Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Explain with diagram, Frenkel defect. What are the conditions for its formation? What is its effect on density and electrical neutrality of the crystal?
Solution
- Frenkel defect:
a. Frenkel defect arises when an ion of an ionic compound is missing from its regular lattice site and occupies an interstitial position between lattice points. The cations are usually smaller than anions. Therefore, the cations occupy interstitial sites.
b. The smaller cation is displaced from its normal site to interstitial space. It, therefore, creates a vacancy defect at its original position and an interstitial defect at its new location in the same crystal. Frenkel defect can be regarded as the combination of vacancy defect and interstitial defect.
c. This defect is found in ionic crystals like ZnS, AgCl, AgBr, AgI and CaF2.
Frenkel defect
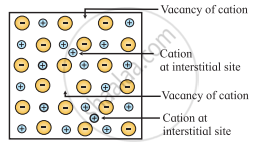
- Conditions for the formation of Frenkel defect:
a. Frenkel defect occurs in ionic compounds with large difference between sizes of cation and anion.
b. The ions of ionic compounds must be having low coordination number.
- Consequences of Frenkel defect:
a. As no ions are missing from the crystal lattice as a whole, the density of solid and its chemical properties remain unchanged.
b. The crystal as a whole remains electrically neutral because the equal numbers of cations and anions are present.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Answer the following in one or two sentences.
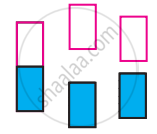
The following pictures show population of bands for materials having different electrical properties. Classify them as insulator, semiconductor or metal.
Answer the following in one or two sentences.
How does the electrical conductivity of a semiconductor change with temperature? Why?
Answer the following in one or two sentences.
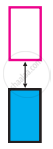
The picture represents bands of MOs for Si. Label valence band, conduction band, and band gap.
Answer the following in brief.
What are valence band and conduction band?
Distinguish with the help of diagrams metal conductors, insulators and semiconductors from each other.
What are n-type semiconductors? Why is the conductivity of doped n-type semiconductor higher than that of pure semiconductor? Explain with diagram.
Which of the following is a metal?
What is band gap? Arrange band gaps in decreasing order for a semiconductor, metal conductor and insulator.
State the conditions for the formation of Schottky defect. The following picture shows bands for materials having different electrical properties.

Classify them as semiconductors, metals and insulators with reason.
Explain the classification of solids on the basis of electrical conductivity.
