Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Figures (a) and (b) refer to the steady flow of a (non-viscous) liquid. Which of the two figures is incorrect? Why?

Solution 1
Figure (a) is incorrect. It is because of the fact that at the kink, the velocity of flow of liquid is large and hence using the Bernoulli’s theorem the pressure is less. As a result, the water should not rise higher in the tube where there is a kink (i.e., where the area of cross-section is small)
Solution 2
(a)
Take the case given in figure (b).
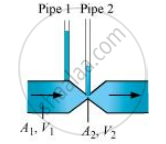
Where,
A1 = Area of pipe1
A2 = Area of pipe 2
V1 = Speed of the fluid in pipe1
V2 = Speed of the fluid in pipe 2
From the law of continuity, we have:
`A_1V_1 = A_2V_2`
When the area of cross-section in the middle of the venturimeter is small, the speed of the flow of liquid through this part is more. According to Bernoulli’s principle, if speed is more, then pressure is less.
Pressure is directly proportional to height. Hence, the level of water in pipe 2 is less.
Therefore, figure (a) is not possible
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Fill in the blanks using the word(s) from the list appended with each statement
For the model of a plane in a wind tunnel, turbulence occurs at a ... speed for turbulence for an actual plane (greater / smaller)
Explain why A spinning cricket ball in air does not follow a parabolic trajectory
In a test experiment on a model aeroplane in a wind tunnel, the flow speeds on the upper and lower surfaces of the wing are 70 m s–1and 63 m s–1 respectively. What is the lift on the wing if its area is 2.5 m2? Take the density of air to be 1.3 kg m–3.
In deriving Bernoulli’s equation, we equated the work done on the fluid in the tube to its change in the potential and kinetic energy. (a) What is the largest average velocity of blood flow in an artery of diameter 2 × 10–3 m if the flow must remain laminar? (b) Do the dissipative forces become more important as the fluid velocity increases? Discuss qualitatively.
A Gipsy car has a canvass top. When the car runs at high speed, the top bulges out. Explain.
Water is flowing through a long horizontal tube. Let PA and PB be the pressures at two points A and B of the tube.
A large number of liquid drops each of radius 'a' are merged to form a single spherical drop of radius 'b'. The energy released in the process is converted into kinetic energy of the big drop formed. The speed of the big drop is [p = density of liquid, T = surface tension of liquid] ____________.
Which of the following is NOT an example of the application of Bernoulli's principle?
Two wires are made of the same material and have the same volume. However wire 1 has cross-sectional area A and wire 2 has cross-sectional area 9A. If the length of wire 1 increases by Δx on applying force F, how much force is needed to stretch wire 2 by the same amount?
A tank is filled with water of density 1 g cm-3 and oil of density 0.9 g cm3. The height of water layer is 100 cm and of the oil layer is 400 cm. If g = 980 cms-2, then the velocity of efflux from an opening in the bottom of the tank is ______.
