Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Filling the blank based on the given relationship.
3 : 1 Monohybrid : : 9 : 3 : 3 : 1 : ______
Solution
3 : 1 Monohybrid : : 9 : 3 : 3 : 1 : Dihybrid cross
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Give Technical Term:
The ratio of offspring on F2 generation in a dihybrid cross.
Complete the following sentence with appropriate word:
_______ is the ratio of dihybrid cross.
In pea plants, yellow seeds are dominant to green. If a heterozygous yellow seed pant is crossed with a green seeded plant, what ratio of yellow and green seeded plants would you expect in the F1 generation?
The genotype of a plant showing the dominant phenotype can be determined by
Define Genetics.
What are the reasons for Mendel’s successes in his breeding experiment?
Identify the statementls that is/are NOT the correct reason/s for Mendel's success in his hybridization experiments.
i. Each factor controlled the single trait and is located on separate chromosomes.
ii. In the pea plant, contrasting characters can be easily recognized.
iii. Mendel carefully recorded the number of plants of each type and expressed his results as ratios.
iv. Mendel performed biochemical assays for identifying the position of 'factors' on chromosome.
A dihybrid condition is ______.
Mendel’s last law is ______.
In a dihybrid cross, F2 phenotypic ratio is 13 : 3. It is case of ______.
Two genes ‘A’ and ‘B’ are linked. In a dihybrid cross involving these two genes, the F1 heterozygote is crossed with homozygous recessive parental type (aa bb). What would be the ratio of offspring in the next generation?
Each gamete carry ______.
Given below is a dihybrid cross performed on Drosophila.
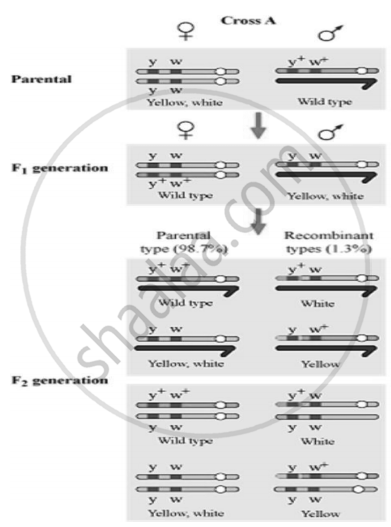
Which of the following conclusions can be drawn on the basis of this cross? When yellow bodied (y), white-eyed (w) Drosophila females were hybridized with brown bodied (y+), red-eyed males (w+) and F1 progenies were intercrossed, F2 generation would have shown the following ratio:
Two pea plants - one with round yellow seeds (RRYY) and another with wrinkled green (rryy) seeds produce F1 progeny that have round, yellow (RrYy) seeds.
When F1 plants are self-pollinated, which new combination of characters is expected in F2 progeny? How many seeds with these new combinations of characters will be produced when a total 160 seeds are produced in F2 generation? Explain with reason.
Sahil performed an experiment to study the inheritance pattern of genes. He crossed tall pea plants (TT) with short pea plants (tt) and obtained all tall plants in F1 generation.
Give a reason why only tall plants are observed in F1 progeny.
Which one of the following genetic ratios will be obtained in a dihybrid test cross:
When two hybrids rrTt and Rrtt are gassed, the phenotype ratio of offspring should be:
Independent assortment means:
Mendel's law of independent assortment is based on F2 ratio of:
