Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Find the maximum magnifying power of a compound microscope having a 25 diopter lens as the objective, a 5 diopter lens as the eyepiece and the separation 30 cm between the two lenses. The least distance for clear vision is 25 cm.
Solution
For the compound microscope, we have:
Power of the objective lens = 25 D
The focal length of the objective lens is given by
`f_0 = 1/(25 D) = 0.04 m = 4 cm`
Power of the eyepiece = 5 D
The focal length of the eyepiece is given by
`f_e = 1/(5D) =0.2 m =20 cm`
Least distance of clear vision, D = 25 cm
Separation between the objective and the eyepiece, L = 30 cm
Magnifying power is maximum when the image is formed by the eyepiece at the least distance of clear vision, i.e., D = 25 cm.
For the eyepiece, we have:
ve = -25 cm and fe = 20 cm
The lens formula is given by
`1/v_e = 1/u_e + 1/f_e`
`=> 1/u_e = 1/v_e -1/f_e`
`=>1/-25 -1/20= -((4+5))/100`
⇒ ue = `(-100)/9` = 11.11 cm
Let uo and vo be the object and image distance for the objective lens.
So, for the objective lens, the image distance will be
V0 = L - u0
v0 = 30 -11.11
⇒ v0 = 18.89 cm ....(1)
As the image produced is real , v0 =+18.89 cm
`1/u_0 = 1/v_0 -1/f_0`
=`1/18.89 - 1/4 = -0.197`
`u_0 =-5.07 cm` .....(2)
Maximum magnifying power of the compound microscope:
m=`v_0/u_0(1+D/f_e)`
=` -(18.89/-5.07) (1+25/20)`
=3.7225 × 2.25 =8.376
So, the maximum magnifying power of the compound microscope is 8.376.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A biconvex lens with its two faces of equal radius of curvature R is made of a transparent medium of refractive index μ1. It is kept in contact with a medium of refractive index μ2 as shown in the figure.
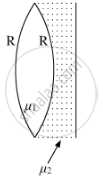
(a) Find the equivalent focal length of the combination.
(b) Obtain the condition when this combination acts as a diverging lens.
(c) Draw the ray diagram for the case μ1 > (μ2 + 1) / 2, when the object is kept far away from the lens. Point out the nature of the image formed by the system.
A biconvex lens made of a transparent material of refractive index 1.5 is immersed in water of refractive index 1.33. Will the lens behave as a converging or a diverging lens? Give reason.
Define the magnifying power?
The size of an object as perceived by an eye depends primarily on
To increase the angular magnification of a simple microscope, one should increase ______.
A simple microscope has a magnifying power of 3.0 when the image is formed at the near point (25 cm) of a normal eye. (a) What is its focal length? (b) What will be its magnifying power if the image is formed at infinity?
A child has near point at 10 cm. What is the maximum angular magnification the child can have with a convex lens of focal length 10 cm?
The magnifying power of a simple microscope is given by `1+D/f` , where D is the least distance for clear vision. For farsighted persons, D is greater than the usual. Does it mean that the magnifying power of a simple microscope is greater for a farsighted person as compared to a normal person? Does it mean that a farsighted person can see an insect more clearly under a microscope than a normal person?
An optical instrument used for angular magnification has a 25 D objective and 20 D eyepiece. The tube length is 25 cm when the eye is least strained. (a) Whether it is a microscope or a telescope? (b) What is the angular magnification produced?
A person wears glasses of power − 2.5 D. Is the person farsighted or nearsighted? What is the far point of person without the glasses?
Magnification for spherical mirrors m is given by ______.
The focal length of the objective of a telescope is 60 cm. To obtain a magnification of 20, the focal length of the eye piece should be:
