Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
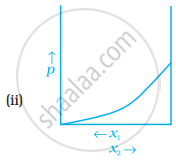
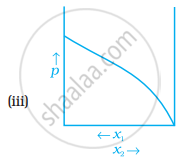
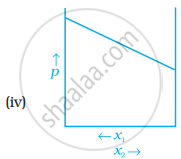
For a binary ideal liquid solution, the variation in total vapour pressure versus composition of solution is given by which of the curves?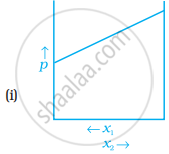
Solution


Explanation:
The slopes at (i) and (iv) are striaght lines, therefore they represent ideal behaviour of the solution.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
30 g of urea (M = 60 g mol−1) is dissolved in 846 g of water. Calculate the vapour pressure of water for this solution if vapour pressure of pure water at 298 K is 23·8 mm Hg.
State Raoult's law for the solution containing volatile components. What is the similarity between Raoult's law and Henry's law?
The vapour pressure of benzene at 30°C is 121.8 mm. By adding 15 g of non-volatile solute in 250 g of benzene, its vapour pressure is decreased to 120.2 mm. The molecular weight of solute is:
The vapour pressure of pure benzene at a certain temperature is 0.850 bar. A non-volatile, nonelectrolyte solid weighing 0.5 g is added to 39.0 g of benzene (molar mass 78 g/mol). The vapour pressure of the solution then is 0.845 bar. What is the molecular mass of the solid substance?
The vapour pressure of pure benzene at 25°C is 640 mm Hg and that of solution of solute A is 630 mm Hg. The molality of a solution is:
The solubility of a solid in a liquid is significantly affected by temperature changes.
\[\ce{Solute + Solvent -> Solution}\]
The system being in a dynamic equilibrium must follow Le-chatelier’s principle.
Considering the Le-chatelier’s principle which of the following is correct?
The vapour pressure of a solvent decreases by 10 mm of Hg when a non-volatile solute was added to the solvent. The mole fraction of the solute in the solution is 0.2. What should be the mole fraction of the solvent if the decrease in the vapour pressure is to be 20 mm of Hg?
Two beakers of capacity 500 mL were taken. One of these beakers, labelled as “A”, was filled with 400 mL water whereas the beaker labelled “B” was filled with 400 mL of 2 M solution of NaCl. At the same temperature both the beakers were placed in closed containers of same material and same capacity as shown in figure.
At a given temperature, which of the following statement is correct about the vapour pressure of pure water and that of NaCl solution.
The vapour pressure of a 5% aqueous solution of non-volatile organic substance at 373 k is 745 mm. calculated the molecular mass of the solute
The vapour pressures of pure liquids A and B are 400 and 600 mm Hg, respectively at 298 K On mixing the two liquids, the sum of their initial volumes is equal to the volume of the final mixture. The mole fraction of liquids B is 0.5 in the mixture. The vapour pressure of the final solution, the mole fractions of components A and B in vapour phase, respectively are ______.
