Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
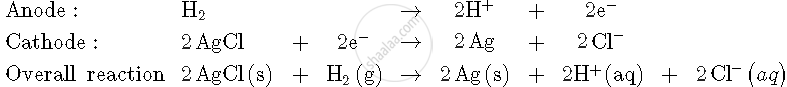
For the reaction
`2AgCl (s) + H_2 (g) ("1 atm") -> 2Ag (s) + 2H^(+) (0.1 M) + 2Cl^(-) (0.1 M)`
`triangleG^0 = -43600 J at 25^@ C`
Calculate the e.m.f. of the cell
`[log 10^(-n) = -n]`
Solution
`triangleG^0 = -nFE_(cell)^0`
`:. E_(cell)^0 = 0.226 V`
`E_(cell) = 0.226 - (0.059)/2 log (0.1)^2 (0.1)^2`
Therefore, `E_(cell) = 0.226 - (0.059)/2 log 10^(-4)`
= 0.226 + 0.059 x 2
= 0.344 V
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
What is the value of for the following reaction at 298 K -
6CO2+ 6H20(l) → C6H1206(s) + 602(g),
Given that: ΔG° = 2879 kj mol-1, AS = -210 JK-1 mol-1.
With the help of the equation ΔG° = - nFEocell. Explain that cell potential is an intensive property.
Calculate ΔrG° for the reaction
Mg (s) + Cu2+ (aq) → Mg2+ (aq) + Cu (s)
Given : E°cell = + 2.71 V, 1 F = 96500 C mol–1
Write any ‘two’ advantages of calomel electrode.
Potential of saturated calomel electrode is-
What is the effect of catalyst on activation energy of a reaction?
The electrical work done in a galvanic cell is equal to ______
The cell potential for the following cell
\[\ce{Pt|H2 (g)| H+ (aq)||Cu^{2+} (0.01 M)| Cu(s)}\]
is 0.576 Vat 298 K. The pH of the solution is ____. (Nearest integer)
The standard Gibbs energy for the given cell reaction in kJ mol-1 at 2'98 K is:
\[\ce{Zn(s) + Cu^{2+} (aq) -> Zn^{2+} (aq) + Cu(s)}\]
E° = 2 V at 298 K
(Faraday's constant, F = 96000 C mol-1)
For a spontaneous reaction, the ΔG, equilibrium constant (K) and `"E"_"cell"^circ` will be respectively.
